PyGMQL: scalable data extraction and analysis for heterogeneous genomic datasets
- PMID: 31703553
- PMCID: PMC6842186
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-019-3159-9
PyGMQL: scalable data extraction and analysis for heterogeneous genomic datasets
Abstract
Background: With the growth of available sequenced datasets, analysis of heterogeneous processed data can answer increasingly relevant biological and clinical questions. Scientists are challenged in performing efficient and reproducible data extraction and analysis pipelines over heterogeneously processed datasets. Available software packages are suitable for analyzing experimental files from such datasets one by one, but do not scale to thousands of experiments. Moreover, they lack proper support for metadata manipulation.
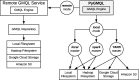
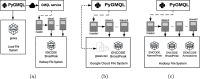
Results: We present PyGMQL, a novel software for the manipulation of region-based genomic files and their relative metadata, built on top of the GMQL genomic big data management system. PyGMQL provides a set of expressive functions for the manipulation of region data and their metadata that can scale to arbitrary clusters and implicitly apply to thousands of files, producing millions of regions. PyGMQL provides data interoperability, distribution transparency and query outsourcing. The PyGMQL package integrates scalable data extraction over the Apache Spark engine underlying the GMQL implementation with native Python support for interactive data analysis and visualization. It supports data interoperability, solving the impedance mismatch between executing set-oriented queries and programming in Python. PyGMQL provides distribution transparency (the ability to address a remote dataset) and query outsourcing (the ability to assign processing to a remote service) in an orthogonal way. Outsourced processing can address cloud-based installations of the GMQL engine.
Conclusions: PyGMQL is an effective and innovative tool for supporting tertiary data extraction and analysis pipelines. We demonstrate the expressiveness and performance of PyGMQL through a sequence of biological data analysis scenarios of increasing complexity, which highlight reproducibility, expressive power and scalability.
Keywords: Data scalability; Distribution transparency; Genomic data; Python; Tertiary data analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Masseroli Marco, Canakoglu Arif, Pinoli Pietro, Kaitoua Abdulrahman, Gulino Andrea, Horlova Olha, Nanni Luca, Bernasconi Anna, Perna Stefano, Stamoulakatou Eirini, Ceri Stefano. Processing of big heterogeneous genomic datasets for tertiary analysis of Next Generation Sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 2018;35(5):729–736. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty688. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaharia M, et al. Apache spark: a unified engine for big data processing. Commun ACM. 2016;59(11):56–65. doi: 10.1145/2934664. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

