Comparative analysis of host resistance to Sarcoptes scabiei var. cuniculi in two different rabbit breeds
- PMID: 31703721
- PMCID: PMC6842134
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-019-3764-5
Comparative analysis of host resistance to Sarcoptes scabiei var. cuniculi in two different rabbit breeds
Abstract
Background: Scabies, caused by infestation of the mite Sarcoptes scabiei, is one of the most severe ectoparasitic diseases in rabbits. Scabies seriously affects the commercial rabbit breeding, causing severe economic losses. Host resistance to S. scabiei is an important factor in further development of the rabbit industry. In the present study, we compared the host resistance to S. scabiei var. cuniculi of a new breed of domestic rabbit propagated by the Sichuan Animal Sciences Academy (QiXing rabbit, QX) compared with that of a traditional rabbit breed in the domestic rabbit industry (IRA rabbit, IRA).
Methods: Both QX and IRA rabbits were experimentally infested with live S. scabiei var. cuniculi mites for 48 h. Then, during the course of four-week experimental infestation period, the body weight of rabbits was recorded every two weeks for calculating body-weight variations in comparison to the non-infested control rabbits. Skin lesions in the foot area were assessed on weekly basis and serum samples were tested weekly for the estimation of changes in the total antibody levels (IgG, IgE and IgM). Moreover, DNA extracted from the blood samples was amplified for analysis of the genetic diversity in the major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ Alpha (MHC-DQA) gene.
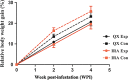
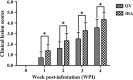
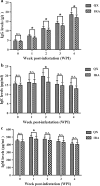
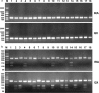
Results: Compared to the IRA rabbits, the QX rabbits showed a significantly higher (P < 0.05) relative body weight gain compared to the non-infested control rabbits and significantly lower (P < 0.05) scores for foot skin lesions and higher levels of IgG, IgE and IgM at weeks 1 to 4, week 2 and week 1 post-infestation, respectively. Furthermore, a polymorphism site at position 103 bp of exon two of MHC-DQA gene and a different gene frequency were found between two rabbit breeds, suggesting the genetic basis for the differential host resistance to the S. scabiei var. cuniculi between two rabbit breeds.
Conclusions: The QX rabbits showed higher host resistance to S. scabiei var. cuniculi compared to the IRA rabbits at the clinical, immunological and genetic levels. These results provide a reference for the breeding of rabbits with adequately improved and sustained host resistance to scabies in the domestic rabbit industry.
Keywords: Antibodies levels; Host resistance; MHC-DQA; Rabbit breeds; Sarcoptes scabiei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of an ELISA using recombinant Ssλ20ΔB3 antigen for the serological diagnosis of Sarcoptes scabiei infestation in domestic and wild rabbits.Vet Parasitol. 2015 Dec 15;214(3-4):315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2015.07.011. Epub 2015 Jul 28. Vet Parasitol. 2015. PMID: 26276579
-
Primary and secondary experimental infestation of rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) with Sarcoptes scabiei from a wild rabbit: factors determining resistance to reinfestation.Vet Parasitol. 2014 Jun 16;203(1-2):173-83. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2014.03.001. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Vet Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24690250
-
The acaricidal efficacy of aqueous neem extract and ivermectin against Sarcoptes scabiei var. cuniculi in experimentally infested rabbits.Parasitol Res. 2013 Jun;112(6):2319-30. doi: 10.1007/s00436-013-3395-2. Epub 2013 Apr 10. Parasitol Res. 2013. PMID: 23572045
-
Sarcoptic mange in domestic rabbits: Pathogenesis, impact, and control strategies.Vet Parasitol. 2025 Jan;333:110357. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2024.110357. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Vet Parasitol. 2025. PMID: 39612697 Review.
-
The immunology of susceptibility and resistance to scabies.Parasite Immunol. 2010 Aug;32(8):532-40. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.2010.01218.x. Parasite Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20626808 Review.
Cited by
-
Non-specific effects of inactivated Mycobacterium bovis oral and parenteral treatment in a rabbit scabies model.Vet Res. 2024 Mar 26;55(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01293-y. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 38532491 Free PMC article.
-
An Antibody Persistent and Protective Two rSsCLP-Based Subunit Cocktail Vaccine against Sarcoptes scabiei in a Rabbit Model.Vaccines (Basel). 2020 Mar 16;8(1):129. doi: 10.3390/vaccines8010129. Vaccines (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32187979 Free PMC article.
-
Essential Oils against Sarcoptes scabiei.Molecules. 2022 Dec 19;27(24):9067. doi: 10.3390/molecules27249067. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36558200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trait Analysis in Domestic Rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus f. domesticus) Using SNP Markers from Genotyping-by-Sequencing Data.Animals (Basel). 2022 Aug 11;12(16):2052. doi: 10.3390/ani12162052. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009642 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aiello SE, Mays A, Amstutz HE. Rabbits. In: Aiello SE, Moses MA, editors. The Merck Veterinary Manual. New Jersey: Merck Inc; 1988. pp. 1386–1396.
-
- Radi ZA. Outbreak of sarcoptic mange and malasseziasis in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) Comp Med. 2004;54:434–437. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

