The UFMylation System in Proteostasis and Beyond
- PMID: 31703843
- PMCID: PMC6917045
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2019.09.005
The UFMylation System in Proteostasis and Beyond
Abstract
Post-translational modifications are at the apex of cellular communication and eventually regulate every aspect of life. The identification of new post-translational modifiers is opening alternative avenues in understanding fundamental cell biology processes and may ultimately provide novel therapeutic opportunities. The ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (UFM1) is a post-translational modifier discovered a decade ago but its biological significance has remained mostly unknown. The field has recently witnessed an explosion of research uncovering the implications of the pathway to cellular homeostasis in living organisms. We overview recent advances in the function and regulation of the UFM1 pathway, and its implications for cell physiology and disease.
Keywords: ER stress; UBL; UFM1; UPR; proteostasis.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



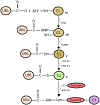
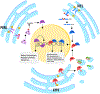
References
-
- Komander D and Rape M (2012) The Ubiquitin Code. Annu. Rev. Biochem, 81, 203–229 - PubMed
-
- Wang M and Kaufman RJ (2016) Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature, 529, 326–335 - PubMed
-
- Hetz C et al. (2013) Targeting the unfolded protein response in disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov, 12, 703–719 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

