Virus-like Vesicles Expressing Multiple Antigens for Immunotherapy of Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 31704650
- PMCID: PMC6889364
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.10.040
Virus-like Vesicles Expressing Multiple Antigens for Immunotherapy of Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
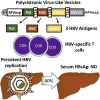
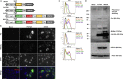
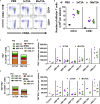
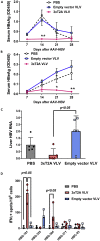
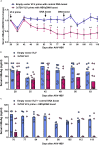
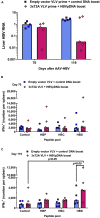
Infections with hepatitis B virus (HBV) can initiate chronic hepatitis and liver injury, causing more than 600,000 deaths each year worldwide. Current treatments for chronic hepatitis B are inadequate and leave an unmet need for immunotherapeutic approaches. We designed virus-like vesicles (VLV) as self-amplifying RNA replicons expressing three HBV antigens (polymerase, core, and middle surface) from a single vector (HBV-VLV) to break immune exhaustion despite persistent HBV replication. The HBV-VLV induces HBV-specific T cells in naive mice and renders them resistant to acute challenge with HBV. Using a chronic model of HBV infection, we demonstrate efficacy of HBV-VLV priming in combination with DNA booster immunization, as 40% of treated mice showed a decline of serum HBV surface antigen below the detection limit and marked reduction in liver HBV RNA accompanied by induction of HBsAg-specific CD8 T cells. These results warrant further evaluation of HBV-VLV for immunotherapy of chronic hepatitis B.
Keywords: Immunology; Medical Microbiology; Virology.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
T.O.Y, S.W.M., B.A., J.K.R., M.D.R., and V. N. have financial relationships with CaroGen Corporation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virus-Like Vesicle-Based Therapeutic Vaccine Vectors for Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection.J Virol. 2015 Oct;89(20):10407-15. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01184-15. Epub 2015 Aug 5. J Virol. 2015. PMID: 26246574 Free PMC article.
-
Heterologous prime-boost immunization with vesiculovirus-based vectors expressing HBV Core antigen induces CD8+ T cell responses in naïve and persistently infected mice and protects from challenge.Antiviral Res. 2019 Aug;168:156-167. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2019.05.014. Epub 2019 May 30. Antiviral Res. 2019. PMID: 31153968 Free PMC article.
-
A Highly Attenuated Vesicular Stomatitis Virus-Based Vaccine Platform Controls Hepatitis B Virus Replication in Mouse Models of Hepatitis B.J Virol. 2019 Feb 19;93(5):e01586-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01586-18. Print 2019 Mar 1. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30541859 Free PMC article.
-
T-cell therapy for chronic viral hepatitis.Cytotherapy. 2017 Nov;19(11):1317-1324. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2017.07.011. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Cytotherapy. 2017. PMID: 28847469 Review.
-
Role of silent hepatitis B virus in chronic hepatitis B surface antigen(-) liver disease.Antiviral Res. 2001 Nov;52(2):117-23. doi: 10.1016/s0166-3542(01)00176-0. Antiviral Res. 2001. PMID: 11672821 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a hybrid alphavirus-SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirion for rapid quantification of neutralization antibodies and antiviral drugs.Cell Rep Methods. 2022 Mar 28;2(3):100181. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2022.100181. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Cell Rep Methods. 2022. PMID: 35229082 Free PMC article.
-
CARG-2020 targets IL-12, IL-17, and PD-L1 pathways to effectively treat melanoma and breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 13;15(1):29649. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14750-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40804279 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Modulation of Innate and Adaptive Responses Restores Immune Surveillance and Establishes Antitumor Immunologic Memory.Cancer Immunol Res. 2024 Feb 2;12(2):261-274. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-23-0127. Cancer Immunol Res. 2024. PMID: 38078853 Free PMC article.
-
Moving Fast Toward Hepatitis B Virus Elimination.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1322:115-138. doi: 10.1007/978-981-16-0267-2_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 34258739 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-based vaccine vectors with distinct replication mechanisms differentially infect and activate dendritic cells.NPJ Vaccines. 2021 Nov 22;6(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41541-021-00400-w. NPJ Vaccines. 2021. PMID: 34811393 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akbar S.M.F., Chen S., Al-Mahtab M., Abe M., Hiasa Y., Onji M. Strong and multi-antigen specific immunity by hepatitis B core antigen (HBcAg)-based vaccines in a murine model of chronic hepatitis B: HBcAg is a candidate for a therapeutic vaccine against hepatitis B virus. Antiviral Res. 2012;96:59–64. - PubMed
-
- Backes S., Jäger C., Dembek C.J., Kosinska A.D., Bauer T., Stephan A.-S., Dišlers A., Mutwiri G., Busch D.H., Babiuk L.A. Protein-prime/modified vaccinia virus Ankara vector-boost vaccination overcomes tolerance in high-antigenemic HBV-transgenic mice. Vaccine. 2016;34:923–932. - PubMed
-
- Chuai X., Chen P., Chen H., Wang W., Deng Y., Ruan L., Li W., Tan W. Protective efficacy and hepatitis B virus clearance in mice enhanced by cell-mediated immunity with novel prime-boost regimens. J. Viral Hepat. 2017;24:337–345. - PubMed
-
- Cova L. Present and future DNA vaccines for chronic hepatitis B treatment. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2017;17:185–195. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

