Steryl Ester Formation and Accumulation in Steroid-Degrading Bacteria
- PMID: 31704679
- PMCID: PMC6952236
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02353-19
Steryl Ester Formation and Accumulation in Steroid-Degrading Bacteria
Abstract
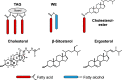
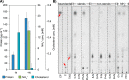
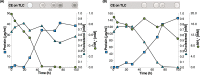
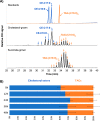
Steryl esters (SEs) are important storage compounds in many eukaryotes and are often prominent components of intracellular lipid droplets. Here, we demonstrate that selected Actino- and Proteobacteria growing on sterols are also able to synthesize SEs and to sequester them in cytoplasmic lipid droplets. We found cholesteryl ester (CE) formation in members of the actinobacterial genera Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium, and Amycolatopsis, as well as several members of the proteobacterial Cellvibrionales order. CEs maximally accumulated under nitrogen-limiting conditions, suggesting that steryl ester formation plays a crucial role for storing excess energy and carbon under adverse conditions. Rhodococcus jostii RHA1 was able to synthesize phytosteryl and cholesteryl esters, the latter reaching up to 7% of its cellular dry weight and 69% of its lipid droplets. Purified lipid droplets from RHA1 contained CEs, free cholesterol, and triacylglycerols. In addition, we found formation of CEs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis when it was grown with cholesterol plus an additional fatty acid substrate. This study provides a basis for the application of bacterial whole-cell systems in the biotechnological production of SEs for use in functional foods and cosmetics.IMPORTANCE Oleaginous bacteria exhibit great potential for the production of high-value neutral lipids, such as triacylglycerols and wax esters. This study describes the formation of steryl esters (SEs) as neutral lipid storage compounds in sterol-degrading oleaginous bacteria, providing a basis for biotechnological production of SEs using bacterial systems with potential applications in the functional food, nutraceutical, and cosmetic industries. We found cholesteryl ester (CE) formation in several sterol-degrading Actino- and Proteobacteria under nitrogen-limiting conditions, suggesting an important role of this process in storing energy and carbon under adverse conditions. In addition, Mycobacterium tuberculosis grown on cholesterol accumulated CEs in the presence of an additional fatty acid substrate.
Keywords: Cellvibrionales; Mycobacterium; Rhodococcus; neutral lipids; sterols; steryl esters.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Fatty Acyl Coenzyme A Reductase Promotes Wax Ester Accumulation in Rhodococcus jostii RHA1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017 Sep 29;83(20):e00902-17. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00902-17. Print 2017 Oct 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28778885 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of nonpolar lipids on the regulation of the steryl ester hydrolases Tgl1p and Yeh1p in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017 Dec;1862(12):1491-1501. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2017.08.009. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017. PMID: 28866104
-
Regulatory link between steryl ester formation and hydrolysis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jul;1851(7):977-86. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.02.011. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25720564
-
Metabolism of Storage Lipids and the Role of Lipid Droplets in the Yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe.Lipids. 2020 Sep;55(5):513-535. doi: 10.1002/lipd.12275. Epub 2020 Sep 15. Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32930427 Review.
-
Lipid droplets and steroidogenic cells.Exp Cell Res. 2016 Jan 15;340(2):209-14. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.11.024. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Exp Cell Res. 2016. PMID: 26639173 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Investigating the causal relationship between the plasma lipidome and cholangiocarcinoma mediated by immune cells: a mediation Mendelian randomization study.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 17;15(1):5807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90140-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39962308 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodococcus strains as a good biotool for neutralizing pharmaceutical pollutants and obtaining therapeutically valuable products: Through the past into the future.Front Microbiol. 2022 Sep 29;13:967127. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.967127. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36246215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid droplets in pathogen infection and host immunity.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Mar;45(3):449-464. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01189-1. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37993536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biogas digestate as a sustainable phytosterol source for biotechnological cascade valorization.Microb Biotechnol. 2023 Feb;16(2):337-349. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14174. Epub 2022 Nov 22. Microb Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36415958 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymatic β-Oxidation of the Cholesterol Side Chain in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Bifurcates Stereospecifically at Hydration of 3-Oxo-cholest-4,22-dien-24-oyl-CoA.ACS Infect Dis. 2021 Jun 11;7(6):1739-1751. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00069. Epub 2021 Apr 7. ACS Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33826843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brigham CJ, Kurosawa K, Rha C, Sinskey AJ. 2011. Bacterial carbon storage to value added products. J Microbiol Biochem Technol S3:002.
-
- Russell NJ, Volkman JK. 1980. The effect of growth temperature on wax ester composition in the psychrophilic bacterium Micrococcus cryophilus ATCC 15174. J Gen Microbiol 118:131–141. doi:10.1099/00221287-118-1-131. - DOI
-
- Kalscheuer R, Stöveken T, Malkus U, Reichelt R, Golyshin PN, Sabirova JS, Ferrer M, Timmis KN, Steinbüchel A. 2007. Analysis of storage lipid accumulation in Alcanivorax borkumensis: evidence for alternative triacylglycerol biosynthesis routes in bacteria. J Bacteriol 189:918–928. doi:10.1128/JB.01292-06. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

