Megalin: A bridge connecting kidney, the renin-angiotensin system, and atherosclerosis
- PMID: 31707037
- PMCID: PMC6980733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104537
Megalin: A bridge connecting kidney, the renin-angiotensin system, and atherosclerosis
Abstract
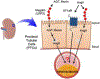
Megalin is a member of the low-density lipoprotein receptor superfamily. It has been recognized as an endocytic receptor for a large spectrum of ligands. As a consequence, megalin regulates homeostasis of many molecules and affects multiple physiological and pathophysiological functions. The renin-angiotensin system is a hormonal system. A number of studies have reported contributions of the renin-angiotensin system to atherosclerosis. There is evolving evidence that megalin is a regulator of the renin-angiotensin system, and contributes to atherosclerosis. This brief review provides contemporary insights into effects of megalin on renal functions, the renin-angiotensin system, and atherosclerosis.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Kidney; Megalin; Renin angiotensin system.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Angiotensinogen and Megalin Interactions Contribute to Atherosclerosis-Brief Report.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019 Feb;39(2):150-155. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311817. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30567480 Free PMC article.
-
Megalin-Mediated Endocytosis in the Kidney Proximal Tubule: Relevance to Regulation of the Renal Renin-Angiotensin System.Nephron. 2023;147(3-4):244-249. doi: 10.1159/000526369. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Nephron. 2023. PMID: 36096093 Review.
-
Megalin, Proton Pump Inhibitors and the Renin-Angiotensin System in Healthy and Pre-Eclamptic Placentas.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 10;22(14):7407. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147407. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299027 Free PMC article.
-
Megalin: a Novel Determinant of Renin-Angiotensin System Activity in the Kidney?Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020 Mar 14;22(4):30. doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-01037-1. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020. PMID: 32172431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-148b regulates megalin expression and is associated with receptor downregulation in mice with unilateral ureteral obstruction.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;313(2):F210-F217. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00585.2016. Epub 2017 Mar 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28331063
Cited by
-
Ciprofloxacin Accelerates Angiotensin-II-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Senescence Through Modulating AMPK/ROS pathway in Aortic Aneurysm and Dissection.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Sep;24(9):889-903. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09892-z. Epub 2024 Aug 13. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39138741 Free PMC article.
-
Internalization of Angiotensin-(1-12) in Adult Retinal Pigment Epithelial-19 Cells.J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2023 May;39(4):290-299. doi: 10.1089/jop.2022.0139. Epub 2023 Mar 21. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. 2023. PMID: 36944130 Free PMC article.
-
Updates on the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and the Cardiovascular Continuum.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 17;12(7):1582. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071582. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Proximal Tubule Cell-specific Megalin Deletion Does Not Affect Atherosclerosis But Induces Tubulointerstitial Nephritis in Mice Fed Western Diet.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 27:2024.05.11.592234. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.11.592234. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2025 Jan;45(1):74-89. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.321366. PMID: 38798535 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Membranous nephropathy: Clearer pathology and mechanisms identify potential strategies for treatment.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1036249. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1036249. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Christensen EI, Birn H. Megalin and cubilin: multifunctional endocytic receptors. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3 (2002) 256–266. - PubMed
-
- Nielsen R, Christensen EI, Birn H. Megalin and cubilin in proximal tubule protein reabsorption: from experimental models to human disease. Kidney Int. 89 (2016) 58–67. - PubMed
-
- Marzolo MP, Farfan P. New insights into the roles of megalin/LRP2 and the regulation of its functional expression. Biol Res. 44 (2011) 89–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

