Nanotechnology in regenerative ophthalmology
- PMID: 31707052
- PMCID: PMC7474549
- DOI: 10.1016/j.addr.2019.10.006
Nanotechnology in regenerative ophthalmology
Abstract
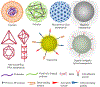
In recent years, regenerative medicine is gaining momentum and is giving hopes for restoring function of diseased, damaged, and aged tissues and organs and nanotechnology is serving as a catalyst. In the ophthalmology field, various types of allogenic and autologous stem cells have been investigated to treat some ocular diseases due to age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, retinitis pigmentosa, diabetic retinopathy, and corneal and lens traumas. Nanomaterials have been utilized directly as nanoscaffolds for these stem cells to promote their adhesion, proliferation and differentiation or indirectly as vectors for various genes, tissue growth factors, cytokines and immunosuppressants to facilitate cell reprogramming or ocular tissue regeneration. In this review, we reviewed various nanomaterials used for retina, cornea, and lens regenerations, and discussed the current status and future perspectives of nanotechnology in tracking cells in the eye and personalized regenerative ophthalmology. The purpose of this review is to provide comprehensive and timely insights on the emerging field of nanotechnology for ocular tissue engineering and regeneration.
Keywords: Cell reprogramming; Electrospun nanofibers; Immunomodulators; Nanoscaffolds; Nanotopography; Ocular regeneration; Self-assembled peptides; Stem cells.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Niloy KK, Gulfam M, Compton K, Li D, Huang GTJ, Lowe TL, Methacrylated Hyaluronan Based Hydrogel Scaffolds with Tunable Mechanical and Biodegradable Properties Maintain Pluripotency Stemness in Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells, Regenerative Engineering and Translational Medicine, First Online: 10 July (2019).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

