Dysregulation of Autophagy, Mitophagy, and Apoptosis Genes in the CA3 Region of the Hippocampus in the Ischemic Model of Alzheimer's Disease in the Rat
- PMID: 31707369
- PMCID: PMC6971835
- DOI: 10.3233/JAD-190966
Dysregulation of Autophagy, Mitophagy, and Apoptosis Genes in the CA3 Region of the Hippocampus in the Ischemic Model of Alzheimer's Disease in the Rat
Abstract
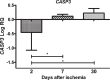
There is currently no knowledge about the expression profile of the autophagy (BECN1), mitophagy (BNIP3), and apoptosis (CASP3) genes in the CA3 region of the hippocampus after cerebral ischemia. In addition, it is unknown whether genes for BECN1, BNIP3, and CASP3 have any effect on the neuronal death in the CA3 area of the hippocampus due to ischemia. In this study, for the first time, we present, by means of a quantitative PCR protocol with reverse transcriptase, the expression of BECN1 and CASP3 genes in the neuronal CA3 region of the hippocampus with the co-expression of the mitochondrial BNIP3 gene, which genes are associated with Alzheimer's disease, in the ischemic model of Alzheimer's disease in the rat. The present study showed that after ischemia, the CASP3 gene was significantly expressed within 7-30 days, the BECN1 gene was significantly overexpressed on the thirtieth day, and the BINP3 gene was lowered below control values during post-ischemic follow-up period. The caspase-dependent neuronal death in the CA3 region of the hippocampus after ischemia is not accompanied by overexpression of the BNIP3 gene. Our data may therefore suggest a new insight into the BNIP3 gene in the regulation of neuronal mitophagy in neurodegeneration in the CA3 region of the hippocampus after ischemia. This indicates no involvement of the BNIP3 gene along with the CASP3 gene in the CA3 region of the hippocampus in delayed neuronal death after brain ischemia.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; apoptosis; autophagy; brain ischemia; cardiac arrest; genes; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors’ disclosures available online (
Figures


Similar articles
-
Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Mitophagy Genes in the CA3 Area in an Ischemic Model of Alzheimer's Disease with 2-Year Survival.J Alzheimers Dis. 2024;99(4):1375-1383. doi: 10.3233/JAD-240401. J Alzheimers Dis. 2024. PMID: 38759019 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Autophagy, Mitophagy, and Apoptotic Genes in the Medial Temporal Lobe Cortex in an Ischemic Model of Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2016 Jul 27;54(1):113-21. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160387. J Alzheimers Dis. 2016. PMID: 27472881 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy, mitophagy and apoptotic gene changes in the hippocampal CA1 area in a rat ischemic model of Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Dec;69(6):1289-1294. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.07.015. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Pharmacol Rep. 2017. PMID: 29128811
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
-
Participation of Amyloid and Tau Protein in Post-Ischemic Neurodegeneration of the Hippocampus of a Nature Identical to Alzheimer's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 28;22(5):2460. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052460. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33671097 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Alzheimer's Disease Connected Genes in the Post-Ischemic Hippocampus and Temporal Cortex.Genes (Basel). 2022 Jun 14;13(6):1059. doi: 10.3390/genes13061059. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35741821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ischemia-Reperfusion Programming of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Genes-A New Perspective on Brain Neurodegeneration after Cardiac Arrest.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 20;25(2):1291. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021291. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279289 Free PMC article.
-
LRP1 and RAGE Genes Transporting Amyloid and Tau Protein in the Hippocampal CA3 Area in an Ischemic Model of Alzheimer's Disease with 2-Year Survival.Cells. 2023 Dec 4;12(23):2763. doi: 10.3390/cells12232763. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067191 Free PMC article.
-
Genes associated with Alzheimer's disease affecting ischemic neurodegeneration of the hippocampal CA3 region.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jul;16(7):1392-1393. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.300982. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33318423 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Crosstalk between the aging intestinal microflora and the brain in ischemic stroke.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 6;14:998049. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.998049. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36275012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sadowski M, Wisniewski HM, Jakubowska-Sadowska K, Tarnawski M, Lazarewicz JW, Mossakowski MJ (1999) Pattern of neuronal loss in the rat hippocampus following experimental cardiac arrest-induced ischemia. J Neurol Sci 168, 13–20. - PubMed
-
- Pluta R (2000) The role of apolipoprotein E in the deposition of β-amyloid peptide during ischemia-reperfusion brain injury. A model of early Alzheimer’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 903, 324–334. - PubMed
-
- Pluta R, Ułamek M, Jabłoński M (2009) Alzheimer’s mechanisms in ischemic brain degeneration. Anat Rec 292, 1863–1881. - PubMed
-
- Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Mavroudis I, Fotiou D, Baloyannis S (2012) Hippocampal neuronal loss in the CA1 and CA3 areas of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Psychiatr Danub 24, 152–158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

