Effect of mountain ultra-marathon running on plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 and lipid profile in healthy trained men
- PMID: 31707478
- PMCID: PMC6969869
- DOI: 10.1007/s00421-019-04256-w
Effect of mountain ultra-marathon running on plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 and lipid profile in healthy trained men
Abstract
Purpose: Angiopoietin-like protein 4 (ANGPTL4) regulates lipid metabolism by inhibiting lipoprotein lipase activity and stimulating lipolysis in adipose tissue. The aim of this study was to find out whether the mountain ultra-marathon running influences plasma ANGPTL4 and whether it is related to plasma lipid changes.
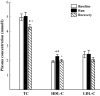
Methods: Ten healthy men (age 31 ± 1.1 years) completed a 100-km ultra-marathon running. Plasma ANGPTL4, free fatty acids (FFA), triacylglycerols (TG), glycerol (Gly), total cholesterol (TC), low (LDL-C) and high (HDL-C) density lipoprotein-cholesterol were determined before, immediately after the run and after 90 min of recovery.
Results: Plasma ANGPTL4 increased during exercise from 68.0 ± 16.5 to 101.2 ± 18.1 ng/ml (p < 0.001). This was accompanied by significant increases in plasma FFA, Gly, HDL-C and decreases in plasma TG concentrations (p < 0.01). After 90 min of recovery, plasma ANGPTL4 and TG did not differ significantly from the exercise values, while plasma FFA, Gly, TC and HDL-C were significantly lower than immediately after the run. TC/HDL-C and TG/HDL-C molar ratios were significantly reduced. The exercise-induced changes in plasma ANGPTL4 correlated positively with those of FFA (r = 0.73; p < 0.02), and HDL-C (r = 0.69; p < 0.05). Positive correlation was found also between plasma ANGPTL4 and FFA concentrations after 90 min of recovery (r = 0.77; p < 0.01).
Conclusions: The present data suggest that increase in plasma FFA during mountain ultra-marathon run may be involved in plasma ANGPTL4 release and that increase in ANGPTL4 secretion may be a compensatory mechanism against fatty acid-induced oxidative stress. Increase in plasma HDL-C observed immediately after the run may be due to the protective effect of ANGPTL4 on HDL.
Keywords: ANGPTL4; Cholesterol; Free fatty acids; Triacylglycerols; Ultra-marathon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
ANGPTL4, IL-6 and TNF-α as regulators of lipid metabolism during a marathon run.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;12(1):19940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17439-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36402848 Free PMC article.
-
Growth hormone upregulates ANGPTL4 mRNA and suppresses lipoprotein lipase via fatty acids: Randomized experiments in human individuals.Metabolism. 2020 Apr;105:154188. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154188. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Metabolism. 2020. PMID: 32084431
-
Plasma angiopoietin-like 4 is related to phospholipid transfer protein activity in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects: role of enhanced low grade inflammation.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Mar 27;17(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0717-5. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29587751 Free PMC article.
-
The influence of exercise on the concentrations of triglyceride and cholesterol in human plasma.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984;12:205-44. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984. PMID: 6376133 Review.
-
Potential Role of ANGPTL4 in the Cross Talk between Metabolism and Cancer through PPAR Signaling Pathway.PPAR Res. 2017;2017:8187235. doi: 10.1155/2017/8187235. Epub 2017 Jan 15. PPAR Res. 2017. PMID: 28182091 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating Antimicrobial Peptides as Biomarkers of Inflammation and Airway Dysfunction After Marathon Running.Biology (Basel). 2025 Jul 7;14(7):825. doi: 10.3390/biology14070825. Biology (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723384 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic communication during exercise.Nat Metab. 2020 Sep;2(9):805-816. doi: 10.1038/s42255-020-0258-x. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Nat Metab. 2020. PMID: 32747791 Review.
-
ANGPTL4, IL-6 and TNF-α as regulators of lipid metabolism during a marathon run.Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 19;12(1):19940. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17439-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36402848 Free PMC article.
-
Beetroot juice - a suitable post-marathon metabolic recovery supplement?J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021 Dec 3;18(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12970-021-00468-8. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34861868 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Muscle thickness and inflammation during a 50km ultramarathon in recreational runners.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 1;17(9):e0273510. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273510. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36048789 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achten J, Venables MC, Jeukendrup AE. Fat oxidation rates are higher during running compared with cycling over a wide range of intensities. Metabolism. 2003;52:747–752. - PubMed
-
- Capostagno B, Bosch A. Higher fat oxidation in running than cycling at the same exercise intensities. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2010;20:44–55. - PubMed
-
- Catoire M, Alex S, Paraskevopulos N, Mattijssen F, Evers-van Gogh I, Schaart G, Jeppesen J, Kneppers A, Mensink M, Voshol PJ, Olivecrona G, Tan NS, Hesselink MK, Berbée JF, Rensen PC, Kalkhoven E, Schrauwen P, Kersten S. Fatty acid-inducible ANGPTL4 governs lipid metabolic response to exercise. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:E1043–E1052. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

