Engineering Allostery into Proteins
- PMID: 31707711
- PMCID: PMC7508002
- DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13-8719-7_15
Engineering Allostery into Proteins
Abstract
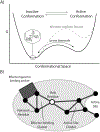
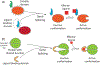
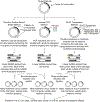
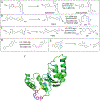
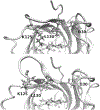
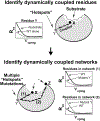
Our ability to engineer protein structure and function has grown dramatically over recent years. Perhaps the next level in protein design is to develop proteins whose function can be regulated in response to various stimuli, including ligand binding, pH changes, and light. Endeavors toward these goals have tested and expanded on our understanding of protein function and allosteric regulation. In this chapter, we provide examples from different methods for developing new allosterically regulated proteins. These methods range from whole insertion of regulatory domains into new host proteins, to covalent attachment of photoswitches to generate light-responsive proteins, and to targeted changes to specific amino acid residues, especially to residues identified to be important for relaying allosteric information across the protein framework. Many of the examples we discuss have already found practical use in medical and biotechnology applications.
Keywords: Allostery; Amino acid network; Covalent modification; Domain insertion; Energy landscape; Protein engineering; Protein regulation.
Figures

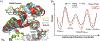
Similar articles
-
Structurally distributed surface sites tune allosteric regulation.Elife. 2021 Jun 16;10:e68346. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68346. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34132193 Free PMC article.
-
Design and engineering of allosteric communications in proteins.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022 Apr;73:102334. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2022.102334. Epub 2022 Feb 15. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2022. PMID: 35180676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineered control of enzyme structural dynamics and function.Protein Sci. 2018 Apr;27(4):825-838. doi: 10.1002/pro.3379. Epub 2018 Feb 16. Protein Sci. 2018. PMID: 29380452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Domain insertion permissibility-guided engineering of allostery in ion channels.Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 17;10(1):290. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08171-0. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30655517 Free PMC article.
-
Profiling of engineering hotspots identifies an allosteric CRISPR-Cas9 switch.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 Jun;34(6):646-51. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3528. Epub 2016 May 2. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27136077 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Distinct conformational dynamics and allosteric networks in alpha tryptophan synthase during active catalysis.Protein Sci. 2021 Mar;30(3):543-557. doi: 10.1002/pro.4011. Epub 2020 Dec 19. Protein Sci. 2021. PMID: 33314435 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxation and single site multiple mutations to identify and control allosteric networks.Methods. 2023 Aug;216:51-57. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2023.06.002. Epub 2023 Jun 9. Methods. 2023. PMID: 37302521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein Function Analysis through Machine Learning.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 6;12(9):1246. doi: 10.3390/biom12091246. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36139085 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying and controlling inactive and active conformations of a serine protease.Sci Adv. 2025 Apr 11;11(15):eadu7447. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu7447. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Sci Adv. 2025. PMID: 40203097 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical methods to map and quantify allosteric motions in human glucokinase.Methods Enzymol. 2023;685:433-459. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2023.03.009. Epub 2023 Apr 19. Methods Enzymol. 2023. PMID: 37245911 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Axe JM, Yezdimer EM, O’Rourke KF, Kerstetter NE, You W, Chang CE, Boehr DD (2014) Amino acid networks in a (beta/alpha) (8) barrel enzyme change during catalytic turnover. J Am Chem Soc 136(19):6818–6821 - PubMed
-
- Berliner L (2015) Protein NMR: modern techniques and biomedical applications
-
- Blackmore NJ, Reichau S, Jiao W, Hutton RD, Baker EN, Jameson GB, Parker EJ (2013) Three sites and you are out: ternary synergistic allostery controls aromatic amino acid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Biol 425(9):1582–1592 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

