Identification and Analyses of Extra-Cranial and Cranial Rhabdoid Tumor Molecular Subgroups Reveal Tumors with Cytotoxic T Cell Infiltration
- PMID: 31708418
- PMCID: PMC6905433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.10.013
Identification and Analyses of Extra-Cranial and Cranial Rhabdoid Tumor Molecular Subgroups Reveal Tumors with Cytotoxic T Cell Infiltration
Abstract
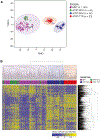
Extra-cranial malignant rhabdoid tumors (MRTs) and cranial atypical teratoid RTs (ATRTs) are heterogeneous pediatric cancers driven primarily by SMARCB1 loss. To understand the genome-wide molecular relationships between MRTs and ATRTs, we analyze multi-omics data from 140 MRTs and 161 ATRTs. We detect similarities between the MYC subgroup of ATRTs (ATRT-MYC) and extra-cranial MRTs, including global DNA hypomethylation and overexpression of HOX genes and genes involved in mesenchymal development, distinguishing them from other ATRT subgroups that express neural-like features. We identify five DNA methylation subgroups associated with anatomical sites and SMARCB1 mutation patterns. Groups 1, 3, and 4 exhibit cytotoxic T cell infiltration and expression of immune checkpoint regulators, consistent with a potential role for immunotherapy in rhabdoid tumor patients.
Keywords: HOX dysregulation; Malignant rhabdoid tumor; SMARCB1; atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumor; cytotoxic T cell infiltration; genomic and epigenomic dysregulation; molecular subgroups; pediatric cancer; tumor-infiltrating immune cells.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Bessho Y, Miyoshi G, Sakata R, and Kageyama R (2001). Hes7: a bHLH-type repressor gene regulated by Notch and expressed in the presomitic mesoderm. Genes Cells 6, 175–185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

