Prognostic Value of Programmed Cell Death Ligand-1 Expression in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of 1,315 Patients
- PMID: 31709181
- PMCID: PMC6823255
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01111
Prognostic Value of Programmed Cell Death Ligand-1 Expression in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis of 1,315 Patients
Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) remains controversial. Therefore, we conducted this meta-analysis to understand the role of PD-L1 in NPC. Method: We searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library up to April 2019. We determined the pooled hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to assess the relationship between PD-L1 and various survival outcomes. Begg's funnel plot was used to assess any publication bias. Results: Eleven studies involving 1,315 patients were included in this meta-analysis. For overall survival (OS), the HR was 1.48 and 95% CI was 1.00-2.18 (p = 0.049). For disease-free survival (DFS), the HR was 1.51 and 95% CI was 0.85-2.69 (p = 0.162). For distant metastasis-free survival (DMFS), the HR was 1.75 and 95% CI was 0.64-4.79 (p = 0.277). For local recurrence-free survival (LRFS), the HR was 0.67 and 95% CI was 0.06-8.16 (p = 0.756). The results of prognosis of PD-L1 and OS were more significant after sensitivity analysis. The pooled odds ratio indicated that PD-L1 expression was not associated with T stage, N stage, M stage, overall stage, sex, age, smoking, or alcohol intake. No publication bias was found. Conclusion: Our meta-analysis showed that PD-L1 overexpression in NPC was associated with a poor OS and may be useful as a novel prognostic factor for NPC.
Keywords: PD-L1; clinical use; meta-analysis; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2019 Liu, Shan, Song and Du.
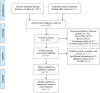
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased programmed death ligand-1 expression predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Onco Targets Ther. 2016 Aug 2;9:4805-13. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S110713. eCollection 2016. Onco Targets Ther. 2016. PMID: 27536144 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and clinicopathological value of PD-L1 in colorectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 May 14;12:3671-3682. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S190168. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31190869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The prognostic significance of PD-L1 and PD-1 expression in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cancer Cell Int. 2019 May 22;19:141. doi: 10.1186/s12935-019-0863-5. eCollection 2019. Cancer Cell Int. 2019. PMID: 31139018 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Role of Programmed Death-Ligand 1 in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Laryngoscope. 2020 Nov;130(11):2598-2606. doi: 10.1002/lary.28523. Epub 2020 Feb 29. Laryngoscope. 2020. PMID: 32112431
-
Prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: a meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1119168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1119168. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37138876 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The clinical prognostic value of PD-L1 after concurrent chemoradiotherapy in Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Nov;9(22):1650. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-5175. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34988159 Free PMC article.
-
LAPTM4B promotes the progression of nasopharyngeal cancer.Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021 Jun 1;21(3):305-312. doi: 10.17305/bjbms.2020.4738. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 32651973 Free PMC article.
-
The clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of programmed death-ligand 1 in prostate cancer: a meta-analysis of 3133 patients.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 9;13(2):2279-2293. doi: 10.18632/aging.202248. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33318295 Free PMC article.
-
TGF-β1-Mediated PD-L1 Glycosylation Contributes to Immune Escape via c-Jun/STT3A Pathway in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 4;12:815437. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.815437. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35311117 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of PD-L1 expression in patients with anal cancer: a meta-analysis.Biomark Med. 2024;18(7):333-344. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2023-0727. Epub 2024 May 3. Biomark Med. 2024. PMID: 38700275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen L, Hu CS, Chen XZ, Hu GQ, Cheng ZB, Sun Y, et al. . Concurrent chemoradiotherapy plus adjuvant chemotherapy versus concurrent chemoradiotherapy alone in patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a phase 3 multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. (2012) 13:163–71. 10.1016/S1470-2045(11)70320-5 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

