Digital cholangioscopy in a patient with biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
- PMID: 31709346
- PMCID: PMC6834971
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vgie.2019.07.007
Digital cholangioscopy in a patient with biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
Keywords: BT-IPMN, biliary tract intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.
Figures

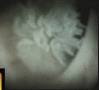

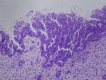
Similar articles
-
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the biliary tract: a real disease?HPB (Oxford). 2009 Dec;11(8):684-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1477-2574.2009.00122.x. HPB (Oxford). 2009. PMID: 20495637 Free PMC article.
-
A comparison between intraductal papillary neoplasms of the biliary tract (BT-IPMNs) and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas (P-IPMNs) reveals distinct clinical manifestations and outcomes.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013 Jun;39(6):554-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.02.016. Epub 2013 Mar 15. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23506840
-
Comparative radiological pathological study of biliary intraductal tubulopapillary neoplasm and biliary intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017 Oct;42(10):2460-2469. doi: 10.1007/s00261-017-1167-7. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017. PMID: 28470400
-
Intraductal neoplasms of the bile duct. A new challenge to biliary tract tumor pathology.Histol Histopathol. 2017 Oct;32(10):1001-1015. doi: 10.14670/HH-11-892. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Histol Histopathol. 2017. PMID: 28337739 Review.
-
A novel approach to biliary tract pathology based on similarities to pancreatic counterparts: is the biliary tract an incomplete pancreas?Pathol Int. 2010 Jun;60(6):419-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2010.02543.x. Pathol Int. 2010. PMID: 20518896 Review.
Cited by
-
Unconventional treatment of inoperable biliary IPMN with an oesophageal stent in the common bile duct: case report.Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc. 2023 Jul 31;16:26317745231183311. doi: 10.1177/26317745231183311. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Gastrointest Endosc. 2023. PMID: 37533690 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ruiz A., Vedel B., Fabre C. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts (IPMN-B) Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2016;40:370–372. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

