Cell-free DNA fetal fraction in twin gestations in single-nucleotide polymorphism-based noninvasive prenatal screening
- PMID: 31711265
- PMCID: PMC7027570
- DOI: 10.1002/pd.5609
Cell-free DNA fetal fraction in twin gestations in single-nucleotide polymorphism-based noninvasive prenatal screening
Abstract
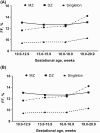
Objectives: The performance of noninvasive prenatal screening (NIPS) for fetal aneuploidy in twin pregnancies is dependent on the amount of placentally derived cell-free DNA, the "fetal fraction (FF)," present in maternal plasma. We report FF values in monozygotic (MZ) and dizygotic (DZ) pregnancies.
Methods: We reviewed FF in pregnancies at 10 to 20 completed weeks gestational age based on single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP)-based NIPS where zygosity was routinely established in twin pregnancies. The cohort included 121 446 (96.3%) singleton, 1454 (1.2%) MZ, and 3161 (2.5%) DZ pregnancies. For DZ twins, individual FFs were measured.
Results: Combined FF for DZ and MZ fetuses were 35% and 26% greater than singletons, respectively. The individual FF contributions from each fetus in DZ twins were, on average, 32% less than singletons. FF in DZ twin pairs were moderately correlated (Pearson correlation coefficient.66). When a threshold of 2.8% FF was applied to define uninterpretable results, 1.7% (2102/121 446) of singletons, 0.8% (11/1454) of MZ pairs, and 5.6% (178/3161) of DZ pairs were uninterpretable.
Conclusion: For optimal aneuploidy NIPS in twin pregnancies, zygosity should be established and in DZ twins FF for both fetuses should be determined to identify those cases where results can be reliably interpreted.
© 2019 The Authors. Prenatal Diagnosis published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Zachary Demko and Paul Billings are employees of Natera, Inc and hold stock in the company. Kimberly Martin and Peter Benn are consultants to Natera and hold stock options. Herman Hedriana is a former employee of Natera and does not own stock or hold stock options. Daniel Salzman serves on the advisory board of Natera; he is not an employee and does not receive any financial compensation from Natera.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a Microhaplotype-Based Noninvasive Prenatal Test in Twin Gestations: Determination of Paternity, Zygosity, and Fetal Fraction.Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 27;12(1):26. doi: 10.3390/genes12010026. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33375453 Free PMC article.
-
Sequencing shorter cfDNA fragments improves the fetal DNA fraction in noninvasive prenatal testing.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019 Oct;221(4):345.e1-345.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2019.05.023. Epub 2019 May 21. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019. PMID: 31125545
-
Noninvasive prenatal screening in twin pregnancies with cell-free DNA using the IONA test: a prospective multicenter study.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Jul;225(1):79.e1-79.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2021.01.005. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 33460583
-
Non-invasive prenatal testing in the management of twin pregnancies.Prenat Diagn. 2021 Sep;41(10):1233-1240. doi: 10.1002/pd.5989. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Prenat Diagn. 2021. PMID: 34170028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early demise of twins in a cohort of stillbirths and second trimester miscarriages.Am J Med Genet A. 2019 Mar;179(3):350-355. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.61014. Epub 2019 Jan 20. Am J Med Genet A. 2019. PMID: 30663217
Cited by
-
Performance of noninvasive prenatal testing for twin pregnancies in South China.J Assist Reprod Genet. 2023 Sep;40(9):2219-2231. doi: 10.1007/s10815-023-02881-1. Epub 2023 Jul 22. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2023. PMID: 37480419 Free PMC article.
-
Zygotic-splitting after in vitro fertilization and prenatal parenthood testing after suspected embryo mix-up - a case report.Int J Legal Med. 2024 Sep;138(5):2057-2064. doi: 10.1007/s00414-024-03245-9. Epub 2024 May 2. Int J Legal Med. 2024. PMID: 38696127 Free PMC article.
-
A Decade of Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) for Chromosomal Abnormalities in Croatia: First National Monocentric Study to Inform Country's Future Prenatal Care Strategy.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 11;15(12):1590. doi: 10.3390/genes15121590. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766857 Free PMC article.
-
Noninvasive detection of twin zygosity using genome-wide linkage disequilibrium information.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Dec;14(12):e70130. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70130. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 39702938 Free PMC article.
-
Non-invasive Prenatal Testing in Pregnancies Following Assisted Reproduction.Curr Genomics. 2022 Nov 18;23(5):326-336. doi: 10.2174/1389202923666220518095758. Curr Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36778193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Green ED, Rubin EM, Olson MV. The future of DNA sequencing. Nature. 2017;550(7675):179‐181. - PubMed
-
- Canick JA, Kloza EM, Lambert‐Messerlian GM, et al. DNA sequencing of maternal plasma to identify Down syndrome and other trisomies in multiple gestations. Prenat Diagn. 2012;32(8):730‐734. - PubMed
-
- Struble CA, Syngelaki A, Oliphant A, Song K, Nicolaides KH. Fetal fraction estimate in twin pregnancies using directed cell‐free DNA analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2014;35(3):199‐203. - PubMed
-
- Nicolaides KH, Musci TJ, Struble CA, Syngelaki A, Gil MM. Assessment of fetal sex chromosome aneuploidy using directed cell‐free DNA analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2014;35(1):1‐6. - PubMed