Efficacy of Bacteriophages in a Staphylococcus aureus Nondiabetic or Diabetic Foot Infection Murine Model
- PMID: 31712203
- PMCID: PMC6985754
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01870-19
Efficacy of Bacteriophages in a Staphylococcus aureus Nondiabetic or Diabetic Foot Infection Murine Model
Abstract
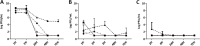
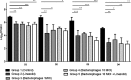
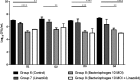
This study investigated the in vivo efficacy of three bacteriophages combined compared with linezolid in two mouse models (nondiabetic and diabetic) of Staphylococcus aureus foot infection. In both models, a single injection of bacteriophages in the hindpaw showed significant antibacterial efficacy. Linezolid was as effective as bacteriophages in nondiabetic animals but ineffective in diabetic animals. These findings further support preclinical and clinical studies for the development of phage therapy.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; bacteriophages; diabetic foot infection; preclinical drug studies.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Lipsky BA, Aragón-Sánchez J, Diggle M, Embil J, Kono S, Lavery L, Senneville É, Urbančič-Rovan V, Van Asten S, International Working Group on the Diabetic Foot, Peters E. 2016. IWGDF guidance on the diagnosis and management of foot infections in persons with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 32 Suppl 1:45–74. doi:10.1002/dmrr.2699. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pouillot F, Chomton M, Blois H, Courroux C, Noelig J, Bidet P, Bingen E, Bonacorsi S. 2012. Efficacy of bacteriophage therapy in experimental sepsis and meningitis caused by a clone O25b:H4-ST131 Escherichia coli strain producing CTX-M-15. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 56:3568–3575. doi:10.1128/AAC.06330-11. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

