Potentiality of forkhead box Q1 as a biomarker for monitoring tumor features and predicting prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 31713908
- PMCID: PMC6977110
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23031
Potentiality of forkhead box Q1 as a biomarker for monitoring tumor features and predicting prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to explore the correlation of forkhead box Q1 (FOXQ1) with clinicopathological features and survival profiles in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: A total of 238 NSCLC patients with TNM stage I-III who underwent surgical resection were reviewed, and the expression of FOXQ1 in tumor and paired adjacent tissue was detected using immunohistochemistry assays. The clinical data and survival data of patients with NSCLC were retrieved and calculated.
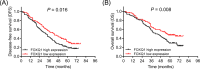
Results: FOXQ1 expression was increased in tumor tissue (61.3% high expression and 38.7% low expression) compared with paired adjacent tissue (37.8% high expression and 62.2% low expression) (P < .001). In addition, high FOXQ1 expression was associated with larger tumor size (P = .042), lymph node metastasis (P = .040), and advanced TNM stage (P = .002). Disease-free survival (DFS) (P = .016) and overall survival (OS) (P = .008) were both reduced in patients with high FOXQ1 expression compared with patients with low FOXQ1 expression. Additionally, high FOXQ1 expression (P = .043), poor pathological differentiation (P = .003), and lymph node metastasis (P < .001) were independent risk factors for DFS, and high FOXQ1 expression (P = .021), tumor size (>5 cm) (P = .014), and lymph node metastasis (P < .001) were independent risk factors for OS.
Conclusion: High FOXQ1 expression is associated with advanced tumor features as well as undesirable survival profiles in patients with NSCLC, implying the potential prognostic value of FOXQ1 for NSCLC.
Keywords: clinicopathological features; forkhead box Q1; non-small cell lung cancer; survival profile.
© 2019 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
AKIP1 expression in tumor tissue as a new biomarker for disease monitoring and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer: Results of a retrospective study.J Clin Lab Anal. 2020 Apr;34(4):e23128. doi: 10.1002/jcla.23128. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Clin Lab Anal. 2020. PMID: 31782840 Free PMC article.
-
FoxQ1 overexpression influences poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer, associates with the phenomenon of EMT.PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039937. Epub 2012 Jun 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22761930 Free PMC article.
-
[Correlation between expression of forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) and clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011 Jun;33(6):426-30. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2011. PMID: 21875482 Chinese.
-
Research progress on the regulation of tumor initiation and development by the forkhead box Q1 gene.J Cancer Res Ther. 2018 Jan;14(1):6-11. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_701_17. J Cancer Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29516951 Review.
-
The roles of MASPIN expression and subcellular localization in non-small cell lung cancer.Biosci Rep. 2020 May 29;40(5):BSR20200743. doi: 10.1042/BSR20200743. Biosci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32391558 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Organoids Model Transcriptional Hallmarks of Oncogenic KRAS Activation in Lung Epithelial Progenitor Cells.Cell Stem Cell. 2020 Oct 1;27(4):663-678.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.07.022. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Cell Stem Cell. 2020. PMID: 32891189 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00887 Acts as an Enhancer RNA to Promote Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Progression by Binding with FOXQ1.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024;24(5):519-533. doi: 10.2174/0115680096258716231026063704. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38804344
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Postmus PE, Kerr KM, Oudkerk M, et al. Early and locally advanced non‐small‐cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow‐up. Ann Oncol. 2017;28(suppl_4):iv1‐iv21. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe SI, Nakagawa K, Suzuki K, et al. Neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy for Stage III non‐small cell lung cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2017;47(12):1112‐1118. - PubMed
-
- Li Y, Zhang Y, Yao Z, Li S, Yin Z, Xu M. Forkhead box Q1: a key player in the pathogenesis of tumors (Review). Int J Oncol. 2016;49(1):51‐58. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

