Toblerone: Surface-Based Partial Volume Estimation
- PMID: 31714217
- PMCID: PMC7291325
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2951080
Toblerone: Surface-Based Partial Volume Estimation
Abstract
Partial volume effects (PVE) present a source of confound for the analysis of functional imaging data. Correction for PVE requires estimates of the partial volumes (PVs) present in an image. These estimates are conventionally obtained via volumetric segmentation, but such an approach may not be accurate for complex structures such as the cortex. An alternative is to use surface-based segmentation, which is well-established within the literature. Toblerone is a new method for estimating PVs using such surfaces. It uses a purely geometric approach that considers the intersection between a surface and the voxels of an image. In contrast to existing surface-based techniques, Toblerone is not restricted to use with any particular structure or modality. Evaluation in a neuroimaging context has been performed on simulated surfaces, simulated T1-weighted MRI images and finally a Human Connectome Project test-retest dataset. A comparison has been made to two existing surface-based methods; in all analyses Toblerone's performance either matched or surpassed the comparator methods. Evaluation results also show that compared to an existing volumetric method (FSL FAST), a surface-based approach with Toblerone offers improved robustness to scanner noise and field non-uniformity, and better inter-session repeatability in brain volume. In contrast to volumetric methods, a surface-based approach negates the need to perform resampling which is advantageous at the resolutions typically used for neuroimaging.
Figures


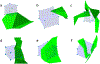


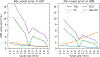


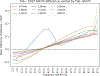
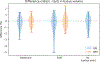

References
-
- Müller-Gärtner HW, Links JM, Prince JL, Bryan RN, McVeigh E, Leal JP, Davatzikos C, and Frost JJ, “Measurement of Radiotracer Concentration in Brain Gray Matter Using Positron Emission Tomography: MRI-Based Correction for Partial Volume Effects,” J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 571–583, July 1992. - PubMed
-
- Asllani I, Borogovac A, and Brown TR, “Regression algorithm correcting for partial volume effects in arterial spin labeling MRI,” Magn. Reson. Med, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 1362–1371, September 2008. - PubMed
-
- Chappell MA, Groves AR, MacIntosh BJ, Donahue MJ, Jezzard P, and Woolrich MW, “Partial volume correction of multiple inversion time arterial spin labeling MRI data,” Magn. Reson. Med, vol. 65, no. 4, pp. 1173–1183, 2011. - PubMed
-
- Shattuck DW, Sandor-Leahy SR, Schaper KA, Rottenberg DA, and Leahy RM, “Magnetic resonance image tissue classification using a partial volume model,” Neuroimage, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 856–876, 2001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

