Hypertension, but not body mass index, is predictive of increased pancreatic lipid content and islet dysfunction
- PMID: 31715064
- PMCID: PMC7103563
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15698
Hypertension, but not body mass index, is predictive of increased pancreatic lipid content and islet dysfunction
Abstract
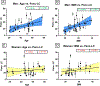
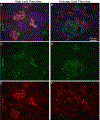
Pancreatic steatosis is thought to be a negative risk factor for pancreas transplant outcomes. Despite considering donor body mass index (BMI) and the visualization of intercalated fat as indicators of donor pancreas lipid content, transplant surgeons do not use a quantitative method to directly measure steatosis when deciding to transplant a pancreas. In this study, we used nondiabetic human pancreata donated for research to measure the pancreatic and islet-specific lipid content to determine which clinical markers correlate best with lipid content. Interestingly, we found that BMI and age correlate with increased pancreatic lipid content (Panc-LC) in men, but not women. Our findings further suggest that total Panc-LC correlates with an increase in islet lipid content for both men and women. We noted that pancreata donated from individuals with a history of hypertension have increased Panc-LC independent of donor BMI or sex. Moreover, we identify hypertension as a risk factor for reduced islet function after islet isolation. Together, our findings emphasize differences in pancreas graft quality related to pancreatic and islet lipid content, which may not be predicted by assessing BMI alone but may be influenced by a donor history of hypertension.
Keywords: basic (laboratory) research/science; donors and donation; hypertension/antihypertensives; organ procurement; organ procurement and allocation; organ transplantation in general; pancreas/simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation; translational research/science.
© 2019 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

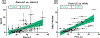

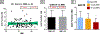
References
-
- Roglic G, World Health Organization. Global report on diabetes. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Collaborators GBDRF, Forouzanfar MH, Alexander L, et al. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2015;386(10010):2287–2323. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gruessner RW, Sutherland DE, Gruessner AC. Mortality assessment for pancreas transplants. Am J Transplant. 2004;4(12):2018–2026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

