Atraumatic splenic rupture in young adult following cocaine use
- PMID: 31715447
- PMCID: PMC6849116
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2019.10.081
Atraumatic splenic rupture in young adult following cocaine use
Abstract
Introduction: Splenic rupture most commonly results from a traumatic mechanism. Spontaneous splenic ruptures are a rare occurrence. This is an interesting and rare case of atraumatic splenic rupture (ASR) presented after sniffing cocaine.
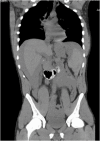
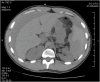
Presentation of case: The patient presented with abdominal pain and tenderness with low hemoglobin on admission. The computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen showed possible spleen rupture with hemoperitoneum. An emergent laparotomy and total splenectomy was performed. The pathology confirmed splenomegaly and a large area of adhesion. Adjacent to the adhesion, a focal disruption of splenic parenchyma was found.
Discussion: ASR has been reported in the literature due to infection, inflammation, mechanical and use of certain drugs. Few cases of ASR have been described due to cocaine use. Splenomegaly is one of the risk factors of ASR. The most probable mechanism of ASR in cocaine use is sudden vasoconstriction, ischemia and infarction of the parenchyma of the spleen, which can result in vascular rupture. Our case of ASR echoes the above process.
Conclusion: Total splenectomy resulted in a good outcome. The patient was discharged home without any services.
Keywords: Atraumatic splenic rupture; Cocaine; Splenomegaly.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Renzulli P., Hostettler A., Schoepfer A.M. Systematic review of atraumatic splenic rupture. Br. J. Surg. 2009;96:1114. - PubMed
-
- Agha R.A., Mimi R., Borrelli M.R., Farwana R., Koshy K., Fowler A.J., Orgill D.P., The SCARE 2018 statement Updating consensus Surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2018;60(December):132–136. - PubMed
-
- Starke K., Montel H., Schümann H.J. Influence of cocaine and phenoxybenzamine on noradrenaline uptake and release. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1971;270(2):210–214. - PubMed
-
- Pitts William R. Cocaine-induced myocardial ischemia and infarction: pathophysiology, recognition, and management. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 1997;40(1):65–76. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials