MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy
- PMID: 31717488
- PMCID: PMC6888406
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20225600
MicroRNA-Based Therapeutic Perspectives in Myotonic Dystrophy
Abstract
Myotonic dystrophy involves two types of chronically debilitating rare neuromuscular diseases: type 1 (DM1) and type 2 (DM2). Both share similarities in molecular cause, clinical signs, and symptoms with DM2 patients usually displaying milder phenotypes. It is well documented that key clinical symptoms in DM are associated with a strong mis-regulation of RNA metabolism observed in patient's cells. This mis-regulation is triggered by two leading DM-linked events: the sequestration of Muscleblind-like proteins (MBNL) and the mis-regulation of the CUGBP RNA-Binding Protein Elav-Like Family Member 1 (CELF1) that cause significant alterations to their important functions in RNA processing. It has been suggested that DM1 may be treatable through endogenous modulation of the expression of MBNL and CELF1 proteins. In this study, we analyzed the recent identification of the involvement of microRNA (miRNA) molecules in DM and focus on the modulation of these miRNAs to therapeutically restore normal MBNL or CELF1 function. We also discuss additional prospective miRNA targets, the use of miRNAs as disease biomarkers, and additional promising miRNA-based and miRNA-targeting drug development strategies. This review provides a unifying overview of the dispersed data on miRNA available in the context of DM.
Keywords: CELF1; MBNL proteins; alternative splicing; antisense oligonucleotides; miRNA-based drug; miRNA-targeting drug; microRNA; myotonic dystrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
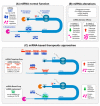
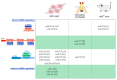
Similar articles
-
The hallmarks of myotonic dystrophy type 1 muscle dysfunction.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2021 Apr;96(2):716-730. doi: 10.1111/brv.12674. Epub 2020 Dec 2. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2021. PMID: 33269537 Review.
-
miR-23b and miR-218 silencing increase Muscleblind-like expression and alleviate myotonic dystrophy phenotypes in mammalian models.Nat Commun. 2018 Jun 26;9(1):2482. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04892-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29946070 Free PMC article.
-
Antagonistic regulation of mRNA expression and splicing by CELF and MBNL proteins.Genome Res. 2015 Jun;25(6):858-71. doi: 10.1101/gr.184390.114. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 25883322 Free PMC article.
-
HNRNPA1-induced spliceopathy in a transgenic mouse model of myotonic dystrophy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Mar 10;117(10):5472-5477. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907297117. Epub 2020 Feb 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32086392 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Approaches for Dominant Muscle Diseases: Highlight on Myotonic Dystrophy.Curr Gene Ther. 2015;15(4):329-37. doi: 10.2174/1566523215666150630120537. Curr Gene Ther. 2015. PMID: 26122101 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA Modifications and RNA Metabolism in Neurological Disease Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 1;22(21):11870. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111870. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proof of concept of peptide-linked blockmiR-induced MBNL functional rescue in myotonic dystrophy type 1 mouse model.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Feb 10;27:1146-1155. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.02.003. eCollection 2022 Mar 8. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35282418 Free PMC article.
-
Myotonic Dystrophy: From Molecular Pathogenesis to Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 8;23(19):11954. doi: 10.3390/ijms231911954. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36233257 Free PMC article.
-
Myotonic Dystrophies: A Genetic Overview.Genes (Basel). 2022 Feb 17;13(2):367. doi: 10.3390/genes13020367. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35205411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatory Potential of Competing Endogenous RNAs in Myotonic Dystrophies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 4;22(11):6089. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116089. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34200099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

