Structure-Function Relationships of the Repeat Domains of RTX Toxins
- PMID: 31718085
- PMCID: PMC6891781
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins11110657
Structure-Function Relationships of the Repeat Domains of RTX Toxins
Abstract
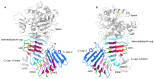
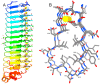
RTX proteins are a large family of polypeptides of mainly Gram-negative origin that are secreted into the extracellular medium by a type I secretion system featuring a non-cleavable C-terminal secretion signal, which is preceded by a variable number of nine-residue tandem repeats. The three-dimensional structure forms a parallel β-roll, where β-strands of two parallel sheets are connected by calcium-binding linkers in such a way that a right-handed spiral is built. The Ca2+ ions are an integral part of the structure, which cannot form without them. The structural determinants of this unique architecture will be reviewed with its conservations and variations together with the implication for secretion and folding of these proteins. The general purpose of the RTX domains appears to act as an internal chaperone that keeps the polypeptide unfolded in the calcium-deprived cytosol and triggers folding in the calcium-rich extracellular medium. A rather recent addition to the structural biology of the RTX toxin is a variant occurring in a large RTX adhesin, where this non-canonical β-roll binds to ice and diatoms.
Keywords: RTX toxin; calcium; internal chaperone; protein folding; tertiary structure; type I secretion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Continuous Assembly of β-Roll Structures Is Implicated in the Type I-Dependent Secretion of Large Repeat-in-Toxins (RTX) Proteins.J Mol Biol. 2020 Sep 18;432(20):5696-5710. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.08.020. Epub 2020 Aug 27. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32860773
-
Characterization of the regions involved in the calcium-induced folding of the intrinsically disordered RTX motifs from the bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase toxin.J Mol Biol. 2010 Mar 26;397(2):534-49. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.01.031. Epub 2010 Jan 22. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 20096704
-
Folding of a synthetic parallel beta-roll protein.FEBS Lett. 2000 Mar 24;470(2):173-7. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(00)01308-9. FEBS Lett. 2000. PMID: 10734229
-
Disorder-to-order transition in the CyaA toxin RTX domain: implications for toxin secretion.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Dec 31;7(1):1-20. doi: 10.3390/toxins7010001. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 25559101 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Calcium-dependent disorder-to-order transitions are central to the secretion and folding of the CyaA toxin of Bordetella pertussis, the causative agent of whooping cough.Toxicon. 2018 Jul;149:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2018.01.007. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Toxicon. 2018. PMID: 29337218 Review.
Cited by
-
Acyl chains stabilize the acylated domain and determine the receptor-mediated interaction of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin with cell membrane.J Biol Chem. 2025 Jul;301(7):110392. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110392. Epub 2025 Jun 19. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40543585 Free PMC article.
-
Almost half of the RTX domain is dispensable for complement receptor 3 binding and cell-invasive activity of the Bordetella adenylate cyclase toxin.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul;297(1):100833. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100833. Epub 2021 May 26. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34051233 Free PMC article.
-
Secrete or perish: The role of secretion systems in Xanthomonas biology.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Dec 24;19:279-302. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.12.020. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 33425257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A serralysin-like protein of Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus modulates components of the bacterial extracellular matrix.Front Microbiol. 2022 Oct 19;13:1006962. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1006962. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36338045 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Spirulina-derived extracellular vesicles and their potential as a vaccine adjuvant.J Extracell Biol. 2024 Dec 12;3(12):e70025. doi: 10.1002/jex2.70025. eCollection 2024 Dec. J Extracell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39676887 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Linhartova I., Osicka R., Bumba L., Masin J., Sebo P. In: Microbial Toxins. Gopalakrishnakone P., Stiles B., Alape-Girón A., Dubreuil J.D., Mandal M., editors. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2015. pp. 1–29.
-
- Welch R.A. RTX Toxin Structure and Function: A Story of Numerous Anomalies and Few Analogies in Toxin Biology. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2001;257:85–111. - PubMed
-
- Linhartová I., Bumba L., Mašín J., Basler M., Osička R., Kamanová J., Procházková K., Adkins I., Hejnová-Holubová J., Sadílková L., et al. RTX proteins: A highly diverse family secreted by a common mechanism. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010;34:1076–1112. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00231.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

