Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort
- PMID: 31719684
- PMCID: PMC6964671
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-019-0619-y
Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort
Abstract
Background: Metastatic breast cancer (MBC) behaviour differs depending on hormone receptors (HR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor (HER2) statuses.
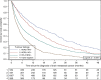
Methods: The kinetics of central nervous system (CNS) metastases (CNS metastasis-free survival, CNSM-FS) and subsequent patient's prognosis (overall survival, OS) according to the molecular subtype were retrospectively assessed in 16703 MBC patients of the ESME nationwide multicentre MBC database (Kaplan-Meier method).
Results: CNS metastases occurred in 4118 patients (24.6%) (7.2% at MBC diagnosis and 17.5% later during follow-up). Tumours were HER2-/HR+ (45.3%), HER2+/HR+ (14.5%), HER2+/HR- (14.9%) and triple negative (25.4%). Median age at CNS metastasis diagnosis was 58.1 years (range: 22.8-92.0). The median CNSM-FS was 10.8 months (95% CI: 16.5-17.9) among patients who developed CNS metastases. Molecular subtype was independently associated with CNSM-FS (HR = 3.45, 95% CI: 3.18-3.75, triple-negative and HER2-/HR+ tumours). After a 30-month follow-up, median OS after CNS metastasis diagnosis was 7.9 months (95% CI: 7.2-8.4). OS was independently associated with subtypes: median OS was 18.9 months (HR = 0.57, 95% CI: 0.50-0.64) for HER2+/HR+ , 13.1 months (HR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.65-0.81) for HER2+/HR-, 4.4 months (HR = 1.55, 95% CI: 1.42-1.69) for triple-negative and 7.1 months for HER2-/HR+ patients (p <0.0001).
Conclusions: Tumour molecular subtypes strongly impact incidence, kinetics and prognosis of CNS metastases in MBC patients.
Clinical trial registration: NCT03275311.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lin NU, Gaspar LE, Soffietti R. Breast cancer in the central nervous system: multidisciplinary considerations and management. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2017;37:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Weathers T, Haney LG, Timmerman R, Dickler M, Shen J, et al. Occult central nervous system involvement in patients with metastatic breast cancer: prevalence, predictive factors and impact on overall survival. Ann. Oncol. 2003;14:1072–1077. - PubMed
-
- Niwińska A, Tacikowska M, Pieńkowski T. Occult brain metastases in HER2-positive breast cancer patients: frequency and response to radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 2007;46:1027–1029. - PubMed
-
- Tsukada Y, Fouad A, Pickren J, Lane W. Central nervous system metastasis from breast carcinoma. Autopsy Study Cancer. 1983;52:2349–2354. - PubMed
-
- Lin NU, Winer EP. Brain metastases: the HER2 paradigm. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007;13:1648–1655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous