Immunohistochemical characterization of oxidative stress in the lungs of rats exposed to the humidifier disinfectant polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride
- PMID: 31719760
- PMCID: PMC6831495
- DOI: 10.1293/tox.2019-0049
Immunohistochemical characterization of oxidative stress in the lungs of rats exposed to the humidifier disinfectant polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride
Abstract
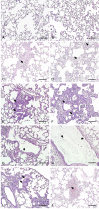
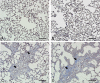
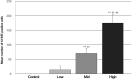
Polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride (PHMG-HCl), an antimicrobial additive in humidifier disinfectants, was associated with the pulmonary disease outbreak in South Korea. However, PHMG-mediated oxidative stress has only been studied in vitro. Here, we evaluated PHMG-induced oxidative stress in the lungs of rats exposed to PHMG-HCl. Male F344 rats were exposed to different concentrations of PHMG-HCl for 13-weeks via whole-body inhalation. Histopathological examination of the exposed rats showed the presence of lung lesions, including alveolar/interstitial fibrosis with inflammatory cell infiltration, bronchioalveolar hyperplasia, bronchiolar/alveolar squamous metaplasia, bronchial/bronchiolar epithelial detachment, and alveolar hemorrhage. Immunohistochemical analysis showed that 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) was expressed in the bronchiolar epithelium, mainly in Clara cells and macrophages of the fibrotic tissue. The number of 4-HNE-positive cells increased significantly in a dose-dependent manner. This is the first in vivo study to report PHMG-induced oxidative stress. Our study provides clues to elucidate the mechanisms underlying PHMG-induced damage in patients affected by humidifier disinfectants.
Keywords: 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE); humidifier disinfectants; immunohistochemistry; inhalation toxicity; oxidative stress; polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride (PHMG-HCl).
©2019 The Japanese Society of Toxicologic Pathology.
Figures

References
-
- Asiedu-Gyekye IJ, Mahmood SA, Awortwe C, and Nyarko AK. A preliminary safety evaluation of polyhexamethylene guanidine hydrochloride. Int J Toxicol. 33: 523–531. 2014. - PubMed
-
- Song JA, Park HJ, Yang MJ, Jung KJ, Yang HS, Song CW, and Lee K. Polyhexamethyleneguanidine phosphate induces severe lung inflammation, fibrosis, and thymic atrophy. Food Chem Toxicol. 69: 267–275. 2014. - PubMed
-
- Park DU, Ryu SH, Lim HK, Kim SK, Choi YY, Ahn JJ, Lee E, Hong SB, Do KH, Cho JL, Bae MJ, Shin DC, Paek DM, and Hong SJ. Types of household humidifier disinfectant and associated risk of lung injury (HDLI) in South Korea. Sci Total Environ. 596-597: 53–60. 2017. - PubMed
-
- Committee on the Investigation of Lung Damage. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Ministry of Health and Welfare, White book on health damage outbreak by humidifier disinfectants. Hanrimwon, Seoul, 2014. (In Korean).
-
- Lee JH, Kim YH, and Kwon JH. Fatal misuse of humidifier disinfectants in Korea: importance of screening risk assessment and implications for management of chemicals in consumer products. Environ Sci Technol. 46: 2498–2500. 2012. - PubMed

