Reduction in pulmonary artery pressures with use of sacubitril/valsartan
- PMID: 31719942
- PMCID: PMC6834956
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jccase.2019.08.006
Reduction in pulmonary artery pressures with use of sacubitril/valsartan
Abstract
Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease (PH-LHD) frequently complicates heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Specific therapies for PH have not offered an advantage in patients with PH-LHD. The combined angiotensin receptor blocker-neprilysin inhibitor (ARNI), sacubitril/valsartan, is a novel therapy that can increase levels of natriuretic peptides (NPs). The resulting action on natriuresis and vasodilation may play an important role in the reduction of pulmonary pressures. Here, we report how the use of ARNI in two patients with HFrEF has resulted in an improvement in PH and, consequently, in clinical status and prognosis. <Learning objective: Sacubitril/valsartan (ARNI) is the newest neurohormonal agent approved for therapy in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Pulmonary hypertension (PH) due to left heart disease (PH-LHD) is frequent in patients with HFrEF and is associated with a reduced functional class and poor prognosis. The use of ARNI has been associated with a relevant reduction in pulmonary pressures in two cases of PH-LHD.>.
Keywords: Heart failure; Pulmonary artery pressures; Sacubitril/valsartan; Systolic dysfunction.
© 2019 Japanese College of Cardiology. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
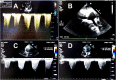
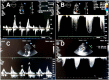
References
-
- Damy T., Goode K.M., Kallvikbacka-Bennett A., Lewinter C., Hobkirk J., Nikitin N.P. Determinants and prognostic value of pulmonary arterial pressure in patients with chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2010;31:2280–2290. - PubMed
-
- Krupicka J., Janota T., Kasalova Z., Hradec J. Natriuretic peptides-physiology, pathophysiology and clinical use in heart failure. Physiol Res. 2009;58:171–177. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

