Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem and piperacillin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxA and exoS transcriptional expression
- PMID: 31719997
- PMCID: PMC6838800
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2019.100608
Effect of subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem and piperacillin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxA and exoS transcriptional expression
Abstract
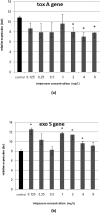
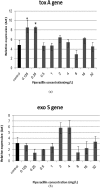
Subinhibitory concentrations (subMIC) of antibiotics, although not able to kill bacteria, can modify their physicochemical characteristics and may interfere with some bacterial functions. This study aimed to investigate the effect of subMIC of imipenem and piperacillin on the transcriptional expression of virulence-related genes toxA and exoS in Pseudomonas auroginosa. Five clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa were screened for the presence of toxA and exoS genes and MICs of imipenem and piperacillin were determined using broth macrodilution. The expression levels of toxA and exoS at subMIC concentrations of antibiotics were measured by real-time PCR. Our results showed that the expression of toxA decreased at all subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem, especially at concentrations 2, 4 and 8 mg/L (p < 0.05). Whereas, exoS expression was increased 4.1- to 7-fold at subinhibitory concentrations of imipenem. The increase of toxA expression was measured at concentrations 16, 4, 2, 0.25 and 0.125 mg/L of piperacillin. However, piperacillin had no significant influence on exoS expression (p > 0.05). Further studies will be required to assess whether subMIC of imipenem can improve the outcomes of severe and serious infections caused by P. aeruginosa.
Keywords: Exoenzyme S; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; exotoxin A; imipenem, piperacillin; subinhibitory concentrations.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates for possible variations within the virulence genes exotoxin A and exoenzyme S.J Surg Res. 1999 Mar;82(1):95-105. doi: 10.1006/jsre.1998.5523. J Surg Res. 1999. PMID: 10068532
-
The Frequency of Exotoxin A and Exoenzymes S and U Genes Among Clinical Isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Shiraz, Iran.Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015 Summer;4(3):167-73. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2015. PMID: 26629485 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular detection of virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa obtained from different clinical specimens in Bandar Abbas.Iran J Microbiol. 2019 Feb;11(1):25-30. Iran J Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30996828 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence, antimicrobial susceptibility, and pathogenic factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in canine clinical samples.Vet World. 2021 Apr;14(4):978-985. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2021.978-985. Epub 2021 Apr 23. Vet World. 2021. PMID: 34083949 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa exoenzyme S, a bifunctional type-III secreted cytotoxin.Int J Med Microbiol. 2000 Oct;290(4-5):381-7. doi: 10.1016/S1438-4221(00)80047-8. Int J Med Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 11111915 Review.
References
-
- Patzer J., Toleman M.A., Deshpande L.M., Ska W.K., Anowska D.D., Bennett P.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains harbouring an unusual blaVIM-4 gene cassette isolated from hospitalized children in Poland (1998–2001) J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004;53:451–456. - PubMed
-
- Khosravi Y., Tee Tay S., Vadivelu J. Analysis of integrons and associated gene cassettes of metallo-β-lactamase-positive Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Malaysia. J Med Microbiol. 2011;60:988–994. - PubMed
-
- Fonseca A.P., Extremina C., Fonseca A.F., Sousa J.C. Effect of subinhibitory concentration of piperacillin/tazobactam on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Med Microbiol. 2004;53:903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
