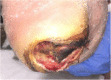
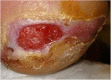
Vehicle ergonomics contributing to a diabetic foot ulcer
- PMID: 31720006
- PMCID: PMC6839194
- DOI: 10.1186/s40842-019-0089-4
Vehicle ergonomics contributing to a diabetic foot ulcer
Abstract
Background: Diabetes mellitus continues to be a rising concern in the United States. It affects an estimated 9.4% of the population and approximately 1.5 million Americans are diagnosed annually. Approximately 85% of diabetic foot ulcers are associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy and an infected diabetic foot ulcer is often the first sign of diabetes. There are countless studies within the literature that investigate how insensate feet and the manifestation of a foot ulcer further decrease quality of life and increase risk for mortality. Literature focuses on gait and kinematics that contribute to the formation of a diabetic foot ulcer. While pressure and shear forces are etiologic factors that may lead to the formation of diabetic foot ulcers, the position of the foot while driving an automobile has been ignored as a possible risk factor.
Case presentation: The clinical case will describe the events of healing a neuropathic diabetic foot ulcer beyond the standard of care treatment plan. It is one of the first case reports to describe vehicle ergonomics as an etiologic factor contributing to a diabetic foot ulcer. Once the patient becomes aware of the unnecessary source of pressure, education and care is provided to manage this likely source of daily pressure to the neuropathic foot.
Conclusion: The article emphasizes the importance of a complete assessment, including nontraditional factors, which may lead to diabetic complications.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus; Diabetic foot; Diabetic foot ulcer; Diabetic peripheral neuropathy; Driving simulator; Pressure.
© The Author(s). 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lower limb biomechanical characteristics of patients with neuropathic diabetic foot ulcers: the diabetes foot ulcer study protocol.BMC Endocr Disord. 2015 Oct 23;15:59. doi: 10.1186/s12902-015-0057-7. BMC Endocr Disord. 2015. PMID: 26499881 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of growth factors for the treatment of chronic wounds in the case of diabetic foot ulcers.GMS Health Technol Assess. 2010 Sep 1;6:Doc12. doi: 10.3205/hta000090. GMS Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 21289885 Free PMC article.
-
Sensory-Motor Mechanisms Increasing Falls Risk in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 May 8;57(5):457. doi: 10.3390/medicina57050457. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34066681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic neuropathic forefoot and heel ulcers: management, clinical presentation and outcomes.J Wound Care. 2015 Sep;24(9):420-5. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2015.24.9.420. J Wound Care. 2015. PMID: 26349023
-
Diabetic foot ulcers: A devastating complication of diabetes mellitus continues non-stop in spite of new medical treatment modalities.World J Diabetes. 2022 Dec 15;13(12):1106-1121. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i12.1106. World J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 36578865 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2017 [cited 17 September 2019]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pdfs/data/statistics/national-diabetes-stat...
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources