Progressive Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Caused by Tic Disorders in a Young Adult with Tourette Syndrome
- PMID: 31720277
- PMCID: PMC6826097
- DOI: 10.13004/kjnt.2019.15.e24
Progressive Cervical Spondylotic Myelopathy Caused by Tic Disorders in a Young Adult with Tourette Syndrome
Abstract
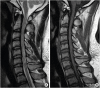
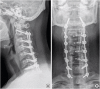
Involuntary movement of the cervical spine can cause damage to the cervical spinal cord. Cervical myelopathy may occur at an early age in involuntary movement disorders, such as tics. We report the case of a 21-year-old man with Tourette syndrome, who developed progressive quadriparesis, which was more severe in the upper extremities. The patient had abnormal motor tics with hyperflexion and hyperextension of the cervical spine for more than 10 years. High-signal intensity intramedullary lesions were observed at C3-4-5-6 level on T2 weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Examinations were performed for high-signal intensity intramedullary lesions that may occur at a young age, but no other diseases were detected. Botulinum toxin injection to the neck musculature and medication for tic disorders were administered. However, the myelopathy was further aggravated, as the involuntary cervical movement still remained. Therefore, laminoplasty was performed at C3-4-5-6, with posterior fixation at C2-3-4-5-6-7 to alleviate the symptoms. The neurological signs and symptoms improved dramatically. The management of tic disorders should be the first priority during treatment. However, surgical treatment may be necessary, if symptoms worsen after appropriate treatment.
Keywords: Spinal cord disease; Spondylosis; Tic disorders; Tourette syndrome.
Copyright © 2019 Korean Neurotraumatology Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adler CH, Zimmerman RS, Lyons MK, Simeone F, Brin MF. Perioperative use of botulinum toxin for movement disorder-induced cervical spine disease. Mov Disord. 1996;11:79–81. - PubMed
-
- Aguirregomozcorta M, Pagonabarraga J, Diaz-Manera J, Pascual-Sedano B, Gironell A, Kulisevsky J. Efficacy of botulinum toxin in severe Tourette syndrome with dystonic tics involving the neck. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2008;14:443–445. - PubMed
-
- Dobbs M, Berger JR. Cervical myelopathy secondary to violent tics of Tourette's syndrome. Neurology. 2003;60:1862–1863. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

