The performance and yield of tuberculosis testing algorithms using microscopy, chest x-ray, and Xpert MTB/RIF
- PMID: 31720409
- PMCID: PMC6830149
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2018.11.002
The performance and yield of tuberculosis testing algorithms using microscopy, chest x-ray, and Xpert MTB/RIF
Abstract
Setting: The introduction of Xpert MTB/RIF (Xpert) and renewed interest in chest x-ray (CXR) for tuberculosis testing has provided additional choices to the smear-based diagnostic algorithms used by TB programs previously. More programmatic data is needed to better understand the implications of possible approaches.
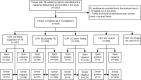
Objective: We sought to evaluate how different testing algorithms using microscopy, Xpert and CXR impacted the number of people detected with TB in a district hospital in Nepal.
Design: Consecutively recruited patients with TB-related symptoms were offered smear microscopy, CXR and Xpert. We tested six hypothetical algorithms and compared yield, bacteriologically positive (Bac+) cases missed, and tests conducted.
Results: Among 929 patients, Bac+ prevalence was 17.3% (n = 161). Smear microscopy detected 121 (75.2% of Bac+). Depending on the radiologists' interpretation of CXR, Xpert testing could be reduced by (31%-60%). Smear microscopy reduced Xpert cartridge need slightly, but increased the overall diagnostic tests performed.
Conclusion: Xpert detected a large proportion of Bac+ TB cases missed by microscopy. CXR was useful in greatly reducing the number of diagnostic tests needed even among presumptive TB patients. Loose CXR readings should be used to identify more people for TB testing. More analysis of costs and standardized CXR reading should be considered.
Keywords: Case detection; Diagnostic algorithms Chest X-ray; Tuberculosis; Xpert MTB/RIF.
© 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization, Global tuberculosis report 2018. Geneva, WHO. 2018.
-
- Corbett E.L., Bandason T., Duong T. Comparison of two active case-finding strategies for community-based diagnosis of symptomatic smear-positive tuberculosis and control of infectious tuberculosis in Harare, Zimbabwe (DETEC TB): a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet. 2010;376(Oct):1244–1253. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uplekar M., Creswell J., Ottmani S.E., Weil D., Sahu S., Lönnroth K. Programmatic approaches to screening for active tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2013;17(Oct (10)):1248–1256. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources