Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific cytokine biomarkers for the diagnosis of childhood TB in a TB-endemic setting
- PMID: 31720428
- PMCID: PMC6830137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jctube.2019.100102
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific cytokine biomarkers for the diagnosis of childhood TB in a TB-endemic setting
Abstract
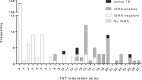
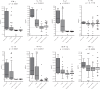
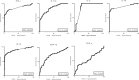
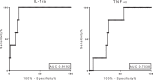
The tuberculin skin test and interferon-gamma release assays have limitations in diagnosing tuberculosis (TB), particularly in children. This study investigated the performance of candidate M. tuberculosis-specific cytokine biomarkers for TB in children in a TB-endemic setting. A total of 237 children with a household contact with smear-positive pulmonary TB were recruited. Importantly, a group of children with illnesses other than TB (sick controls) was included to assess specificity. Median IFN-ɣ, IL-1ra, IL-2, IL-13, IP-10, MIP-1β and TNF-α responses were significantly higher in children with active TB and latent TB infection (LTBI) than in both healthy and sick control children. Three of these cytokines - IL-2, IL-13 and IP-10 - showed better performance characteristics than IFN-ɣ, with IL-2 achieving positive and negative predictive values of 97.7% and 90.7%, respectively. Furthermore, IL-1ra and TNF-α responses differed significantly between active TB and LTBI cases, suggesting that they may be stage-specific biomarkers. Our data indicate that incorporating these biomarkers into future blood-based TB assays could result in substantial performance gains.
Keywords: Cytokine biomarkers; Interferon-gamma release assay; TB-endemic; Tuberculin skin test; Tuberculosis.
© 2019 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . 2018. Global tuberculosis report.http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/274453/9789241565646-eng... (accessed Dec 2018)
-
- Dye C., Scheele S., Dolin P., Pathania V., Raviglione M.C. Consensus statement - global burden of tubercolosis - estimated incidence, prevalence, and mortality by country. JAMA. 1999;282:677–686. - PubMed
-
- Nelson L.J., Wells C.D. Global epidemiology of childhood tuberculosis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8:636–647. - PubMed
-
- Marais B.J., Gie R.P., Schaaf H.S., Hesseling A.C., Obihara C.C., Starke J.J. The natural history of childhood intra-thoracic tuberculosis - a critical review of literature from the pre-chemotherapy era. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2004;8:392–402. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . 2015. The WHO end TB strategy.http://apps.who.int/gb/ebwha/pdf_files/EB134/B134_12-en.pdf?ua=1 (accessed June 2018)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

