Impaired B-cell tolerance checkpoints promote the development of autoimmune diseases and pathogenic autoantibodies
- PMID: 31721234
- PMCID: PMC9145185
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12821
Impaired B-cell tolerance checkpoints promote the development of autoimmune diseases and pathogenic autoantibodies
Abstract
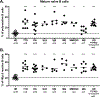
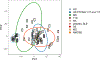
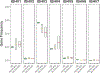
A role for B cells in autoimmune diseases is now clearly established both in mouse models and humans by successful treatment of multiple sclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies that eliminate B cells. However, the underlying mechanisms by which B cells promote the development of autoimmune diseases remain poorly understood. Here, we review evidence that patients with autoimmune disease suffer from defects in early B-cell tolerance checkpoints and therefore fail to counterselect developing autoreactive B cells. These B-cell tolerance defects are primary to autoimmune diseases and may result from altered B-cell receptor signaling and dysregulated T-cell/regulatory T-cell compartment. As a consequence, large numbers of autoreactive naive B cells accumulate in the blood of patients with autoimmune diseases and may promote autoimmunity through the presentation of self-antigen to T cells. In addition, new evidence suggests that this reservoir of autoreactive naive B cells contains clones that may develop into CD27- CD21-/lo B cells associated with increased disease severity and plasma cells secreting potentially pathogenic autoantibodies after the acquisition of somatic hypermutations that improve affinity for self-antigens.
Keywords: B-cell development; autoantibodies; autoimmune disease; immune tolerance checkpoint.
© 2019 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Costa Reis P, Sullivan KE. New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(12):716–730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI142198/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/International
- R01 AI071087/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI114780/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/International
- R56 AI114780/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI061093/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI142198/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI061093/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/International
- U54 NS115054/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AI071087/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases/International
- NS115054/National Institute of Neurological Diseases and Stroke/International
- R01 AI114780/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

