Results of a Multicenter Phase II Study of Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma With Variant Histology and/or Sarcomatoid Features
- PMID: 31721643
- PMCID: PMC7051851
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01882
Results of a Multicenter Phase II Study of Atezolizumab and Bevacizumab for Patients With Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma With Variant Histology and/or Sarcomatoid Features
Abstract
Purpose: In this multicenter phase II trial, we evaluated atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with variant histology or any RCC histology with ≥ 20% sarcomatoid differentiation.
Patients and methods: Eligible patients may have received previous systemic therapy, excluding prior bevacizumab or checkpoint inhibitors. Patients underwent a baseline biopsy and received atezolizumab 1,200 mg and bevacizumab 15 mg/kg intravenously every 3 weeks. The primary end point was overall response rate (ORR) by RECIST version 1.1. Additional end points were progression-free survival (PFS), toxicity, biomarkers of response as determined by programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) status, and on-therapy quality-of-life (QOL) metrics using the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy Kidney Symptom Index-19 and the Brief Fatigue Inventory.
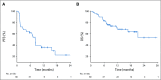
Results: Sixty patients received at least 1 dose of either study agent; the majority (65%) were treatment naïve. The ORR for the overall population was 33% and 50% in patients with clear cell RCC with sarcomatoid differentiation and 26% in patients with variant histology RCC. Median PFS was 8.3 months (95% CI, 5.7 to 10.9 months). PD-L1 status was available for 36 patients; 15 (42%) had ≥ 1% expression on tumor cells. ORR in PD-L1-positive patients was 60% (n = 9) v 19% (n = 4) in PD-L1-negative patients. Eight patients (13%) developed treatment-related grade 3 toxicities. There were no treatment-related grade 4-5 toxicities. QOL was maintained throughout therapy.
Conclusion: In this study, atezolizumab and bevacizumab demonstrated safety and resulted in objective responses in patients with variant histology RCC or RCC with ≥ 20% sarcomatoid differentiation. This regimen warrants additional exploration in patients with rare RCC, particularly those with PD-L1-positive tumors.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02724878.
Figures

Comment in
-
Renal cell carcinoma with non-clear cell histology or sarcomatoid differentiation: recent insight in an unmet clinical need.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jan;9(2):97. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-7009. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33569399 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:354–366. - PubMed
-
- Cheville JC, Lohse CM, Zincke H, et al. Sarcomatoid renal cell carcinoma: An examination of underlying histologic subtype and an analysis of associations with patient outcome. Am J Surg Pathol. 2004;28:435–441. - PubMed
-
- de Velasco G, McKay RR, Lin X, et al. Comprehensive analysis of survival outcomes in non-clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients treated in clinical trials. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2017;15:652–660.e1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

