Changes in CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells and Serum Cytokines in Sublingual and Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis with or without Asthma
- PMID: 31722337
- PMCID: PMC6979435
- DOI: 10.1159/000503143
Changes in CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells and Serum Cytokines in Sublingual and Subcutaneous Immunotherapy in Allergic Rhinitis with or without Asthma
Abstract
Background: Few studies have directly compared the immunologic responses to specific subcutaneous immunotherapy (SCIT) and sublingual immunotherapy (SLIT).
Objective: We aimed to directly compare clinical efficacy and immunological responses between SLIT and SCIT in allergic rhinitis (AR) sensitized to house dust mites.
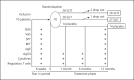
Methods: Sixty-seven patients (age 5-55 years) with moderate-severe Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus (Der-p) and Dermatophagoides farinae AR with or without asthma were randomized (2:2:1) into SLIT (n = 27), SCIT (n = 26) and placebo (n = 14) groups. Symptom and medication scores, visual analogue score, serum Der-p specific immunoglobulin G4 (Der-p-sIgG4), CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) and serum cytokines were measured.
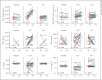
Results: After 1-year treatment, a significant improvement of total rhinitis score (TRS), total rhinitis medication score (TRMS) and visual analogue score occurred in both SLIT and SCIT. There were no differences in clinical efficacy except for TRMS (p = 0.026) when SLIT and SCIT were directly compared. CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ Tregs had a trend towards upregulation in the 2 modes and inversely correlated with TRS (p = 0.024) only in SLIT. Der-p-sIgG4 significantly increased in SLIT and SCIT (p < 0.05), and it was 30 times higher in SCIT than SLIT after the treatment (p < 0.05). Serum interferon-γ significantly increased only in SCIT after 1 (p = 0.008), 6 (p = 0.007) and 12 (p = 0.008) months of treatment and inversely correlated with TRS (p = 0.032).
Conclusion: While SCIT and SLIT have similar rates of clinical improvement, the 2 modes reveal heterogeneous changes of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ Tregs, sIgG4 and cytokines.
Keywords: Allergic rhinitis; Cytokines; Immunoglobulin G4; Regulatory T cells; Subcutaneous immunotherapy; Sublingual immunotherapy.
© 2019 The Author(s)Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Li J, Wang H, Chen Y, Zheng J, Wong GW, Zhong N. House dust mite sensitization is the main risk factor for the increase in prevalence of wheeze in 13- to 14-year-old schoolchildren in Guangzhou city, China. Clin Exp Allergy. 2013 Oct;43((10)):1171–9. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Sun B, Huang Y, Lin X, Zhao D, Tan G, et al. China Alliance of Research on Respiratory Allergic Disease A multicentre study assessing the prevalence of sensitizations in patients with asthma and/or rhinitis in China. Allergy. 2009 Jul;64((7)):1083–92. - PubMed
-
- Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, Denburg J, Fokkens WJ, Togias A, et al. AllerGen Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA) 2008 update (in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2)LEN and AllerGen) Allergy. 2008 Apr;63(Suppl 86):8–160. - PubMed
-
- Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention. 2014. Available from: http://www.ginasthma.org; revised 2014 Vancouver,
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

