Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute high-risk pulmonary embolism: a case series with literature review
- PMID: 31723920
- PMCID: PMC6786667
- DOI: 10.4266/acc.2019.00500
Use of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in patients with acute high-risk pulmonary embolism: a case series with literature review
Abstract
Background: Although extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) has been used for the treatment of acute high-risk pulmonary embolism (PE), there are limited reports which focus on this approach. Herein, we described our experience with ECMO in patients with acute high-risk PE.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed medical records of patients diagnosed with acute high-risk PE and treated with ECMO between January 2014 and December 2018.
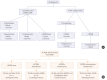
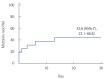
Results: Among 16 patients included, median age was 51 years (interquartile range [IQR], 38 to 71 years) and six (37.5%) were male. Cardiac arrest was occurred in 12 (75.0%) including two cases of out-of-hospital arrest. All patients underwent veno-arterial ECMO and median ECMO duration was 1.5 days (IQR, 0.0 to 4.5 days). Systemic thrombolysis and surgical embolectomy were performed in seven (43.8%) and nine (56.3%) patients, respectively including three patients (18.8%) received both treatments. Overall 30-day mortality rate was 43.8% (95% confidence interval, 23.1% to 66.8%) and 30-day mortality rates according to the treatment groups were ECMO alone (33.3%, n=3), ECMO with thrombolysis (50.0%, n=4) and ECMO with embolectomy (44.4%, n=9).
Conclusions: Despite the vigorous treatment efforts, patients with acute high-risk PE were related to substantial morbidity and mortality. We report our experience of ECMO as rescue therapy for refractory shock or cardiac arrest in patients with PE.
Keywords: embolectomy; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; pulmonary embolism; shock; thrombolytic therapy; treatment outcome.
Copyright © 2019 The Korean Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Aissaoui N, Konstantinides S, Meyer G. What’s new in severe pulmonary embolism? Intensive Care Med. 2019;45:75–7. - PubMed
-
- Konstantinides SV, Torbicki A, Agnelli G, Danchin N, Fitzmaurice D, Galiè N, et al. 2014 ESC guidelines on the diagnosis and management of acute pulmonary embolism. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:3033–69. - PubMed
-
- Jaff MR, McMurtry MS, Archer SL, Cushman M, Goldenberg N, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Management of massive and submassive pulmonary embolism, iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis, and chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123:1788–830. - PubMed
-
- Logan JK, Pantle H, Huiras P, Bessman E, Bright L. Evidencebased diagnosis and thrombolytic treatment of cardiac arrest or periarrest due to suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Emerg Med. 2014;32:789–96. - PubMed
-
- Yusuff HO, Zochios V, Vuylsteke A. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in acute massive pulmonary embolism: a systematic review. Perfusion. 2015;30:611–6. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources