Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Carbapenem Resistance in Gram-negative Bacteria
- PMID: 31724045
- PMCID: PMC6853758
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz824
Epidemiology and Diagnostics of Carbapenem Resistance in Gram-negative Bacteria
Abstract
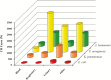
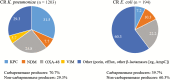
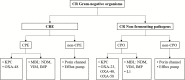
Carbapenem resistance in gram-negative bacteria has caused a global epidemic that continues to grow. Although carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae have received the most attention because resistance was first reported in these pathogens in the early 1990s, there is increased awareness of the impact of carbapenem-resistant nonfermenting gram-negative bacteria, such as Acinetobacter baumannii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. Moreover, evaluating the problem of carbapenem resistance requires the consideration of both carbapenemase-producing bacteria as well as bacteria with other carbapenem resistance mechanisms. Advances in rapid diagnostic tests to improve the detection of carbapenem resistance and the use of large, population-based datasets to capture a greater proportion of carbapenem-resistant organisms can help us gain a better understanding of this urgent threat and enable physicians to select the most appropriate antibiotics.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae; carbapenemases; gram-negative bacteria.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Global priority list of antibiotic-resistant bacteria to guide research, discovery, and development of new antibiotics.2017. Available at: http://www.who.int/medicines/publications/WHO-PPL-Short_Summary_25Feb-ET.... Accessed 1 February 2019.
-
- Cai B, Echols R, Morgan G, et al. . Carbapenem-resistant gram-negative pathogens among hospitalized patients in the United States between 2010 and 2015. Poster presented at: IDWeek 2016, New Orleans, LA,25–30 October 2016; Poster 362.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

