T1 -corrected quantitative chemical shift-encoded MRI
- PMID: 31724776
- PMCID: PMC7047527
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.28062
T1 -corrected quantitative chemical shift-encoded MRI
Abstract
Purpose: To develop and validate a T1 -corrected chemical-shift encoded MRI (CSE-MRI) method to improve noise performance and reduce bias for quantification of tissue proton density fat-fraction (PDFF).
Methods: A variable flip angle (VFA)-CSE-MRI method using joint-fit reconstruction was developed and implemented. In computer simulations and phantom experiments, sources of bias measured using VFA-CSE-MRI were investigated. The effect of tissue T1 on bias using low flip angle (LFA)-CSE-MRI was also evaluated. The noise performance of VFA-CSE-MRI was compared to LFA-CSE-MRI for liver fat quantification. Finally, a prospective pilot study in patients undergoing gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI of the liver to evaluate the ability of the proposed method to quantify liver PDFF before and after contrast.
Results: VFA-CSE-MRI was accurate and insensitive to transmit B1 inhomogeneities in phantom experiments and computer simulations. With high flip angles, phase errors because of RF spoiling required modification of the CSE signal model. For relaxation parameters commonly observed in liver, the joint-fit reconstruction improved the noise performance marginally, compared to LFA-CSE-MRI, but eliminated T1 -related bias. A total of 25 patients were successfully recruited and analyzed for the pilot study. Strong correlation and good agreement between PDFF measured with VFA-CSE-MRI and LFA-CSE-MRI (pre-contrast) was observed before (R2 = 0.97; slope = 0.88, 0.81-0.94 95% confidence interval [CI]; intercept = 1.34, -0.77-1.92 95% CI) and after (R2 = 0.93; slope = 0.88, 0.78-0.98 95% CI; intercept = 1.90, 1.01-2.79 95% CI) contrast.
Conclusion: Joint-fit VFA-CSE-MRI is feasible for T1 -corrected PDFF quantification in liver, is insensitive to B1 inhomogeneities, and can eliminate T1 bias, but with only marginal SNR advantage for T1 values observed in the liver.
Keywords: T1 bias; T1 correction; chemical-shift encoded imaging; fat quantification; hepatic steatosis; liver fat; magnetic resonance imaging; proton density fat-fraction.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures

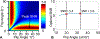
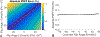



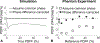

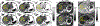
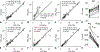
References
-
- Bley TA, Wieben O, Francois CJ, Brittain JH, Reeder SB. Fat and water magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010;31(1):4–18. - PubMed
-
- Liu CY, McKenzie CA, Yu H, Brittain JH, Reeder SB. Fat quantification with IDEAL gradient echo imaging: correction of bias from T(1) and noise. Magn Reson Med 2007;58(2):354–364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

