Pharmacologic epigenetic modulators of alkaline phosphatase in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 31725015
- PMCID: PMC6903384
- DOI: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000570
Pharmacologic epigenetic modulators of alkaline phosphatase in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: In chronic kidney disease (CKD), disturbance of several metabolic regulatory mechanisms cause premature ageing, accelerated cardiovascular disease (CVD), and mortality. Single-target interventions have repeatedly failed to improve the prognosis for CKD patients. Epigenetic interventions have the potential to modulate several pathogenetic processes simultaneously. Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a robust predictor of CVD and all-cause mortality and implicated in pathogenic processes associated with CVD in CKD.
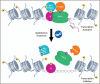
Recent findings: In experimental studies, epigenetic modulation of ALP by microRNAs or bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) protein inhibition has shown promising results for the treatment of CVD and other chronic metabolic diseases. The BET inhibitor apabetalone is currently being evaluated for cardiovascular risk reduction in a phase III clinical study in high-risk CVD patients, including patients with CKD (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT02586155). Phase II studies demonstrate an ALP-lowering potential of apabetalone, which was associated with improved cardiovascular and renal outcomes.
Summary: ALP is a predictor of CVD and mortality in CKD. Epigenetic modulation of ALP has the potential to affect several pathogenetic processes in CKD and thereby improve cardiovascular outcome.
Figures




References
-
- Stenvinkel P, Larsson TE. Chronic kidney disease: a clinical model of premature aging. Am J Kidney Dis 2013; 62:339–351.. - PubMed
-
- Kooman JP, Kotanko P, Schols AM, et al. Chronic kidney disease and premature ageing. Nat Rev Nephrol 2014; 10:732–742.. - PubMed
-
- Millan J. Mammalian alkaline phosphatase: from biology to applications in medicine and biotechnology. Weinheim: Wiley; 2006.
-
- Buchet R, Millan JL, Magne D. Multisystemic functions of alkaline phosphatases. Methods Mol Biol 2013; 1053:27–51.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

