Tobacco Product Use and Cessation Indicators Among Adults - United States, 2018
- PMID: 31725711
- PMCID: PMC6855510
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm6845a2
Tobacco Product Use and Cessation Indicators Among Adults - United States, 2018
Abstract
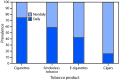
Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of preventable disease and death in the United States (1). The prevalence of adult cigarette smoking has declined in recent years to 14.0% in 2017 (2). However, an array of new tobacco products, including e-cigarettes, has entered the U.S. market (3). To assess recent national estimates of tobacco product use among U.S. adults aged ≥18 years, CDC, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and the National Cancer Institute analyzed data from the 2018 National Health Interview Survey (NHIS). In 2018, an estimated 49.1 million U.S. adults (19.7%) reported currently using any tobacco product, including cigarettes (13.7%), cigars (3.9%), e-cigarettes (3.2%), smokeless tobacco (2.4%), and pipes* (1.0%). Most tobacco product users (83.8%) reported using combustible products (cigarettes, cigars, or pipes), and 18.8% reported using two or more tobacco products. The prevalence of any current tobacco product use was higher in males; adults aged ≤65 years; non-Hispanic American Indian/Alaska Natives; those with a General Educational Development certificate (GED); those with an annual household income <$35,000; lesbian, gay, or bisexual adults; uninsured adults; those with a disability or limitation; and those with serious psychological distress. The prevalence of e-cigarette and smokeless tobacco use increased during 2017-2018. During 2009-2018, there were significant increases in all three cigarette cessation indicators (quit attempts, recent cessation, and quit ratio). Implementing comprehensive population-based interventions in coordination with regulation of the manufacturing, marketing, and distribution of all tobacco products can reduce tobacco-related disease and death in the United States (1,4).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. The health consequences of smoking—50 years of progress: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2014. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/data_statistics/sgr/50th-anniversary/index.htm
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services. E-cigarette use among youth and young adults: a report of the Surgeon General. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2016. https://e-cigarettes.surgeongeneral.gov/documents/2016_SGR_Full_Report_n...
-
- CDC. Best practices for comprehensive tobacco control programs—2014. Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC; 2014. https://www.cdc.gov/tobacco/stateandcommunity/best_practices/index.htm?s...
-
- National Center for Health Statistics. National Health Interview Survey: survey description. Hyattsville, MD: US Department of Health and Human Services, CDC, National Center for Health Statistics; 2018. ftp://ftp.cdc.gov/pub/Health_Statistics/NCHS/Dataset_Documentation/NHIS/...

