Economic evaluation studies in the field of HIV/AIDS: bibliometric analysis on research development and scopes (GAPRESEARCH)
- PMID: 31727059
- PMCID: PMC6854742
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-019-4613-0
Economic evaluation studies in the field of HIV/AIDS: bibliometric analysis on research development and scopes (GAPRESEARCH)
Abstract
Background: The rapid decrease in international funding for HIV/AIDS has been challenging for many nations to effectively mobilize and allocate their limited resources for HIV/AIDS programs. Economic evaluations can help inform decisions and strategic planning. This study aims to examine the trends and patterns in economic evaluation studies in the field of HIV/AIDS and determine their research landscapes.
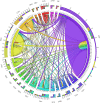
Methods: Using the Web of Science databases, we synthesized the number of papers and citations on HIV/AIDS and economic evaluation from 1990 to 2017. Collaborations between authors and countries, networks of keywords and research topics were visualized using frequency of co-occurrence and Jaccards' similarity index. A Latent Dirichlet Allocation (LDA) analysis to categorize papers into different topics/themes.
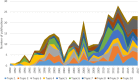
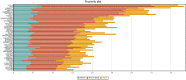
Results: A total of 372 economic evaluation papers were selected, including 351 cost-effectiveness analyses (CEA), 11 cost-utility analyses (CUA), 12 cost-benefit analyses (CBA). The growth of publications, their citations and usages have increased remarkably over the years. Major research topics in economic evaluation studies consisted of antiretroviral therapy (ART) initiation and treatment; drug use prevention interventions and prevention of mother-to-child transmission interventions. Moreover, lack of contextualized evidence was found in specific settings with high burden HIV epidemics, as well as emerging most-at-risk populations such as trans-genders or migrants.
Conclusion: This study highlights the knowledge and geographical discrepancies in HIV/AIDS economic evaluation literature. Future research directions are also informed for advancing economic evaluation in HIV/AIDS research.
Keywords: Bibliometric; Content analysis; Economic evaluation; HIV/AIDS; Health economics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Bach Tran is a member of the editorial board of BMC Health Services Research. HCT is supported by the Wellcome Trust [089276/B/09/7].
Figures

Similar articles
-
Social network and HIV/AIDS: A bibliometric analysis of global literature.Front Public Health. 2022 Nov 2;10:1015023. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1015023. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36408016 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking among people living with HIV/AIDS: a bibliometric analysis (GAPRESEARCH).AIDS Rev. 2022;25(3):105-114. doi: 10.24875/AIDSRev.19000098. AIDS Rev. 2022. PMID: 36343589
-
A Global Bibliometric Analysis of Services for Children Affected by HIV/AIDS: Implications for Impact Mitigation Programs (GAPRESEARCH).AIDS Rev. 2020;22(1):34-43. doi: 10.24875/AIDSRev.19000078. AIDS Rev. 2020. PMID: 32167503
-
Exploring socio-economic dimensions in HIV research: a comprehensive bibliometric analysis (1992-2024).Glob Health Action. 2025 Dec;18(1):2474787. doi: 10.1080/16549716.2025.2474787. Epub 2025 Mar 12. Glob Health Action. 2025. PMID: 40071324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of Interdisciplinary Landscapes of HIV/AIDS Studies from 1983 to 2017: Results from the Global Analysis for Policy in Research (GAPRESEARCH).AIDS Rev. 2019;21(4):184-194. doi: 10.24875/AIDSRev.19000083. AIDS Rev. 2019. PMID: 31834329
Cited by
-
Health related quality of life of people receiving highly active antiretroviral therapy in Southwest Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 20;15(8):e0237013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0237013. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32818950 Free PMC article.
-
A global bibliometric analysis of intimate partner violence in the field of HIV/AIDS: implications for interventions and research development.Front Public Health. 2023 Jun 15;11:1105018. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1105018. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37397707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Cost-Effectiveness of HIV/STI Prevention in High-Income Countries with Concentrated Epidemic Settings: A Scoping Review.AIDS Behav. 2022 Jul;26(7):2279-2298. doi: 10.1007/s10461-022-03583-y. Epub 2022 Jan 15. AIDS Behav. 2022. PMID: 35034238 Free PMC article.
-
Collaboration Network and Trends of Global Coronavirus Disease Research: A Scientometric Analysis.IEEE Access. 2021 Mar 17;9:45001-45016. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3066450. eCollection 2021. IEEE Access. 2021. PMID: 34812387 Free PMC article.
-
HIV Rapid Testing in the General Population and the Usefulness of PrEP in Ecuador: A Cost-Utility Analysis.Front Public Health. 2022 Jun 17;10:884313. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.884313. eCollection 2022. Front Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35784197 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dieleman JL, Haakenstad A, Micah A, Moses M, Abbafati C, Acharya P, Adhikari TB, Adou AK, Ahmad Kiadaliri A, Alam K, et al. Spending on health and HIV/AIDS: domestic health spending and development assistance in 188 countries, 1995–2015. Lancet. 2018;391(10132):1799–1829. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)30698-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global HIV & AIDS statistics — 2019 fact sheet. https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet. Accessed 3 Sept 2019.
-
- Snapshot - HIV investment. http://www.unaids.org/sites/default/files/media_asset/HIV_investments_Sn.... Accessed 3 Sept 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

