Brain surgery in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitor and whole brain radiotherapy for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases
- PMID: 31728013
- PMCID: PMC6856342
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-53456-z
Brain surgery in combination with tyrosine kinase inhibitor and whole brain radiotherapy for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastases
Abstract
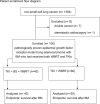
The role of brain surgery (BS) on the survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and brain metastases (BM), particularly those with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations under tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is yet to be defined. We aimed to investigate whether BS could improve the survival of patients in addition to the combination of TKIs and whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT). A cohort of 1394 NSCLC patients between 2011 and 2016 was retrospectively studied. One hundred patients with BM receiving TKI + RT were enrolled. Forty patients (40%) received TKI + BS + RT, and 60 patients (60%) received TKI + RT. Survival time was calculated from the date of BM diagnoses to the date of death or last follow-up. With a median follow-up of 25.6 months (95% CI, 18.6-35.7), the median survival after BM was 18.2 months (95% CI, 10.8 to 27.4) in the TKI + BS + RT group and 11.8 months (95% CI, 5.2 to18) in the TKI + RT group. Cox proportional hazards regression model for the patients with the largest BM over 1 cm showed that TKI + BS + RT group was associated with improved survival relative to TKI + RT group (HR, 0.49; 95% CI, 0.29 to 0.83; P = 0.008). BS adds significant survival benefits in addition to TKIs and WBRT, especially for patients with EGFR-mutant NSCLC and the largest BM over 1 cm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of EGFR-TKIs combined with intracranial radiotherapy in EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients with brain metastases: a retrospective multi-institutional analysis.Radiat Oncol. 2025 Jan 9;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13014-024-02578-4. Radiat Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39789554 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Brain Metastases in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Multi-Institutional Analysis.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Apr 1;35(10):1070-1077. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.7144. Epub 2017 Jan 23. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28113019
-
Clinical outcome of tyrosine kinase inhibitors alone or combined with radiotherapy for brain metastases from epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 21;8(8):13304-13311. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14515. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28076323 Free PMC article.
-
First-line treatment with TKI plus brain radiotherapy versus TKI alone in EGFR-mutated non-small cell Lung cancer with brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Cancer. 2023 Oct 30;23(1):1043. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11548-0. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37904083 Free PMC article.
-
A Neuro-oncologist's Perspective on Management of Brain Metastases in Patients with EGFR Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017 Apr;18(4):22. doi: 10.1007/s11864-017-0466-0. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28391420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor microenvironment and exosomes in brain metastasis: Molecular mechanisms and clinical application.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 20;12:983878. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.983878. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36338717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Management of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Brain Metastases, and Actionable Genomic Alterations: A Systematic Literature Review.Adv Ther. 2024 May;41(5):1815-1842. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02799-9. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38509433 Free PMC article.
-
Revisiting the Role of Surgical Resection for Brain Metastasis.Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2023 Jan;11(1):1-7. doi: 10.14791/btrt.2022.0028. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36762802 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

