Comprehensive Analysis of the Chitinase Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): From Gene Identification and Evolution to Expression in Response to Fusarium oxysporum
- PMID: 31731414
- PMCID: PMC6861899
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20215309
Comprehensive Analysis of the Chitinase Gene Family in Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.): From Gene Identification and Evolution to Expression in Response to Fusarium oxysporum
Abstract
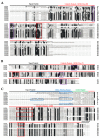
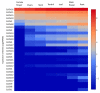
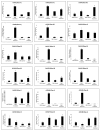
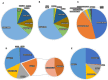
Chitinases, a subgroup of pathogenesis-related proteins, are responsible for catalyzing the hydrolysis of chitin. Accumulating reports indicate that chitinases play a key role in plant defense against chitin-containing pathogens and are therefore good targets for defense response studies. Here, we undertook an integrated bioinformatic and expression analysis of the cucumber chitinases gene family to identify its role in defense against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cucumerinum. A total of 28 putative chitinase genes were identified in the cucumber genome and classified into five classes based on their conserved catalytic and binding domains. The expansion of the chitinase gene family was due mainly to tandem duplication events. The expression pattern of chitinase genes was organ-specific and 14 genes were differentially expressed in response to F. oxysporum challenge of fusarium wilt-susceptible and resistant lines. Furthermore, a class I chitinase, CsChi23, was constitutively expressed at high levels in the resistant line and may play a crucial role in building a basal defense and activating a rapid immune response against F. oxysporum. Whole-genome re-sequencing of both lines provided clues for the diverse expression patterns observed. Collectively, these results provide useful genetic resource and offer insights into the role of chitinases in cucumber-F. oxysporum interaction.
Keywords: Cucumis sativus; Fusarium oxysporum; chitinase; gene expression; gene family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jain K.K., Kumar A., Shankar A., Pandey D., Chaudhary B., Sharma K.K. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly and Protein Profiling of Copper-Induced Lignocellulolytic Fungus Ganoderma Lucidum MDU-7 Reveals Genes Involved in Lignocellulose Degradation and Terpenoid Biosynthetic Pathways. Genomics. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2019.01.012. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang S., Ye X., Chen J., Rao P. A Novel Chitinase Isolated from Vicia Faba and Its Antifungal Activity. Food Res. Int. 2012;45:116–122. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2011.10.010. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 6184043/Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation
- 2018YFD1000800/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- CEFF-PXM2019_014207_000032/The Construction of Beijing Science and Technology Innovation and Service Capacity in Top Subjects
- BAIC01-2016/Project of Beijing Agricultural Innovation Consortium
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

