Depletion of KNL2 Results in Altered Expression of Genes Involved in Regulation of the Cell Cycle, Transcription, and Development in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 31731608
- PMCID: PMC6888302
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20225726
Depletion of KNL2 Results in Altered Expression of Genes Involved in Regulation of the Cell Cycle, Transcription, and Development in Arabidopsis
Abstract
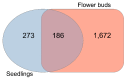
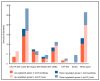
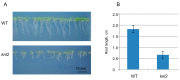
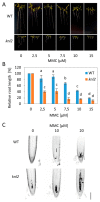
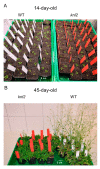
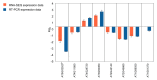
Centromeres contain specialized nucleosomes at which histone H3 is partially replaced by the centromeric histone H3 variant cenH3 that is required for the assembly, maintenance, and proper function of kinetochores during mitotic and meiotic divisions. Previously, we identified a KINETOCHORE NULL 2 (KNL2) of Arabidopsis thaliana that is involved in the licensing of centromeres for the cenH3 recruitment. We also demonstrated that a knockout mutant for KNL2 shows mitotic and meiotic defects, slower development, reduced growth rate, and fertility. To analyze an effect of KNL2 mutation on global gene transcription of Arabidopsis, we performed RNA-sequencing experiments using seedling and flower bud tissues of knl2 and wild-type plants. The transcriptome data analysis revealed a high number of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in knl2 plants. The set was enriched in genes involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, transcription, development, and DNA damage repair. In addition to comprehensive information regarding the effects of KNL2 mutation on the global gene expression, physiological changes in plants are also presented, which provides an integrated understanding of the critical role played by KNL2 in plant growth and development.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; KNL2; RNA-seq; centromere; kinetochores.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

