Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes
- PMID: 31731719
- PMCID: PMC6915406
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9111623
Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes
Abstract
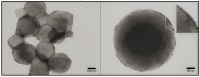
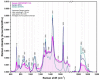
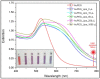
By carefully controlling the electrostatic interactions between cationic liposomes, which already incorporate magnetic nanoparticles in the bilayers, and anionic gold nanoparticles, a new class of versatile multifunctional nanohybrids (plasmonic magneto-liposomes) that could have a major impact in drug delivery and controlled release applications has been synthesized. The experimental results confirmed the successful synthesis of hydrophobic superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) and polyethylene glycol functionalized (PEGylated) gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The SPIONs were incorporated in the liposomal lipidic bilayers, thus promoting the formation of cationic magnetoliposomes. Different concentrations of SPIONs were loaded in the membrane. The cationic magnetoliposomes were decorated with anionic PEGylated gold nanoparticles using electrostatic interactions. The successful incorporation of SPIONs together with the modifications they generate in the bilayer were analyzed using Raman spectroscopy. The plasmonic properties of the multifunctional nanohybrids were investigated using UV-Vis absorption and (surface-enhanced) Raman spectroscopy. Their hyperthermic properties were recorded at different frequencies and magnetic field intensities. After the synthesis, the nanosystems were extensively characterized in order to properly evaluate their potential use in drug delivery applications and controlled release as a result of the interaction with an external stimulus, such as an NIR laser or alternating magnetic field.
Keywords: gold nanoparticles; hyperthermia; magneto-liposomes; multifunctional nanohybrids; superparamagnetic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

