Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31731749
- PMCID: PMC6895916
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11111798
Tumor Mutational Burden and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
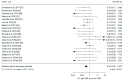
Tumor mutational burden (TMB) is a genomic biomarker that predicts favorable responses to immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs). Here, we set out to assess the predictive value of TMB on long-term survival outcomes in patients undergoing ICIs. We systematically searched PubMed, Embase, CENTRAL and clinicaltrials.gov from inception to 6 August 2019. We included retrospective studies or clinical trials of ICIs that reported hazard ratios (HRs) for overall survival (OS) and/or progression-free survival (PFS) according to TMB. Data on 5712 patients from 26 studies were included. Among patients who received ICIs, high TMB groups showed better OS (HR 0.53, 95% CI 0.42 to 0.67) and PFS (HR 0.52, 95% CI 0.40 to 0.67) compared to low TMB groups. In patients with high TMB, those who received ICIs had a better OS (HR 0.69, 95% CI 0.50 to 0.95) and PFS (HR = 0.66, 95% CI = 0.47 to 0.92) compared to those who received chemotherapy alone, while in patients with low TMB, such ICI benefits of OS or PFS were not statistically significant. In conclusion, TMB may be an effective biomarker to predict survival in patients undergoing ICI treatment. The role of TMB in identifying patient groups who may benefit from ICIs should be determined in future randomized controlled trials.
Keywords: CTLA-4 inhibitor; PD-1 inhibitor; PD-L1 inhibitor; hazard ratio; immune checkpoint inhibitors; overall survival; progression-free survival; tumor mutational burden.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wei S.C., Duffy C.R., Allison J.P. Fundamental Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:1069–1086. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-0367. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials