Lupus Podocytopathy: An Overview
- PMID: 31733721
- PMCID: PMC8405037
- DOI: 10.1053/j.ackd.2019.08.011
Lupus Podocytopathy: An Overview
Abstract
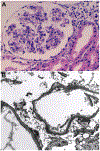
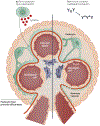
In systemic lupus erythematosus, nephrotic-range proteinuria typically signals the presence of a proliferative lupus nephritis (class III/IV) and/or membranous lupus nephritis (class V, with or without concomitant class III or IV lesions). However, in rare instances, systemic lupus erythematosus patients with nephrotic syndrome have kidney biopsy findings of normal glomeruli or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis lesions, with or without mesangial proliferation, on light microscopy; the absence of subepithelial or subendothelial deposits on immunofluorescence and electron microscopy; and diffuse foot process effacement on electron microscopy. This pattern, termed lupus podocytopathy, is a unique form of lupus nephritis that mimics minimal change disease or primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis and represents approximately 1% of lupus nephritis biopsies. Here we review the clinical features, histological manifestations, diagnostic criteria and classification, pathogenesis, treatment, and prognosis of lupus podocytopathy.
Keywords: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; Lupus nephritis; Lupus podocytopathy; Minimal change disease; Systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2019 National Kidney Foundation, Inc. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Financial Disclosure: The authors declare that they have no relevant financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kraft SW, Schwartz MM, Korbet SM, Lewis EJ. Glomerular podocytopathy in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16(1):175–179. - PubMed
-
- Dube GK, Markowitz GS, Radhakrishnan J, Appel GB, D’agati VD. Minimal change disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Nephrol. 2002;57(2):120–126. - PubMed
-
- Weening JJ, D’agati VD, Schwartz MM, et al.The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004;65(2):521–530. - PubMed
-
- Abuelo JG, Esparza AR, Garella S. Steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome in lupus nephritis. Response to chlorambucil. Arch Intern Med. 1984;144(12):2411–2412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

