Recent Efforts to Dissect the Genetic Basis of Alcohol Use and Abuse
- PMID: 31733789
- PMCID: PMC7071963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2019.09.011
Recent Efforts to Dissect the Genetic Basis of Alcohol Use and Abuse
Abstract
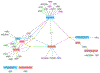
Alcohol use disorder (AUD) is defined by several symptom criteria, which can be dissected further at the genetic level. Over the past several years, our understanding of the genetic factors influencing alcohol use and abuse has progressed tremendously; numerous loci have been implicated in different aspects of alcohol use. Previously known associations with alcohol-metabolizing enzymes (ADH1B, ALDH2) have been replicated definitively. In addition, novel associations with loci containing the genes KLB, GCKR, CRHR1, and CADM2 have been reported. Downstream analyses have leveraged these genetic findings to reveal important relationships between alcohol use behaviors and both physical and mental health. AUD and aspects of alcohol misuse have been shown to overlap strongly with psychiatric disorders, whereas aspects of alcohol consumption have shown stronger links to metabolism. These results demonstrate that the genetic architecture of alcohol consumption only partially overlaps with the genetics of clinically defined AUD. We discuss the limitations of using quantitative measures of alcohol use as proxy measures for AUD, and we outline how future studies will require careful phenotype harmonization to properly capture the genetic liability to AUD.
Keywords: AUDIT; Alcohol consumption; Alcohol-metabolizing genes; Alcoholism; Genetics; Genome-wide association studies.
Copyright © 2019 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

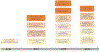


Comment in
-
Advancing Alcohol Genetics Research: One Genome-wide Association Study at a Time and Beyond.Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 1;87(7):590-591. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.01.003. Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32164913 No abstract available.
References
-
- Degenhardt L, Charlson F, Ferrari A, Santomauro D, Erskine H, Mantilla-Herrara A, et al. (2018): The global burden of disease attributable to alcohol and drug use in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. The Lancet Psychiatry. 5: 987–1012. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (2017): Key substance use and mental health indicators in the United States: Results from the 2016 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (HHS Publication No. SMA 17–5044, NSDUH Series H-52). Rockville, MD: Center for Behavioral Health Statistics and Quality, Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

