Lumen Expansion Facilitates Epiblast-Primitive Endoderm Fate Specification during Mouse Blastocyst Formation
- PMID: 31735667
- PMCID: PMC6912163
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2019.10.011
Lumen Expansion Facilitates Epiblast-Primitive Endoderm Fate Specification during Mouse Blastocyst Formation
Abstract
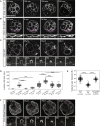
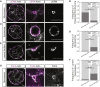
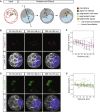
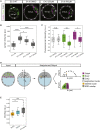
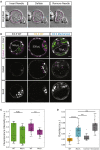
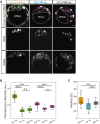
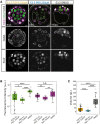
Epithelial tissues typically form lumina. In mammalian blastocysts, in which the first embryonic lumen forms, many studies have investigated how the cell lineages are specified through genetics and signaling, whereas potential roles of the fluid lumen have yet to be investigated. We discover that in mouse pre-implantation embryos at the onset of lumen formation, cytoplasmic vesicles are secreted into intercellular space. The segregation of epiblast and primitive endoderm directly follows lumen coalescence. Notably, pharmacological and biophysical perturbation of lumen expansion impairs the specification and spatial segregation of primitive endoderm cells within the blastocyst. Luminal deposition of FGF4 expedites fate specification and partially rescues the reduced specification in blastocysts with smaller cavities. Combined, our results suggest that blastocyst lumen expansion plays a critical role in guiding cell fate specification and positioning, possibly mediated by luminally deposited FGF4. Lumen expansion may provide a general mechanism for tissue pattern formation.
Keywords: FGF signaling; cell fate specification; cell sorting; early mammalian development; epiblast; lumenogenesis; mouse blastocyst; primitive endoderm; self-organization; vesicle release.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Primitive endoderm differentiation: from specification to epithelium formation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Dec 5;369(1657):20130537. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0537. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25349446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling controls ICM maturation and proper epiblast and primitive endoderm specification in mice.Dev Cell. 2025 Jan 20;60(2):204-219.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.001. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39461340
-
ETV4 and ETV5 orchestrate FGF-mediated lineage specification and epiblast maturation during early mouse development.Development. 2025 Mar 15;152(6):dev204278. doi: 10.1242/dev.204278. Epub 2025 Mar 24. Development. 2025. PMID: 40007475 Free PMC article.
-
[Epiblast and primitive endoderm cell specification during mouse preimplantation development: a combination between biology and mathematical modeling].Med Sci (Paris). 2016 Feb;32(2):192-7. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20163202013. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Med Sci (Paris). 2016. PMID: 26936177 Review. French.
-
FGF4 is required for lineage restriction and salt-and-pepper distribution of primitive endoderm factors but not their initial expression in the mouse.Development. 2013 Jan 15;140(2):267-79. doi: 10.1242/dev.084996. Epub 2012 Nov 28. Development. 2013. PMID: 23193166 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanics of Development.Dev Cell. 2021 Jan 25;56(2):240-250. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.11.025. Epub 2020 Dec 14. Dev Cell. 2021. PMID: 33321105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Wnt-dependent master regulator NKX1-2 controls mouse pre-implantation development.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 May 14;19(5):689-709. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.04.004. Epub 2024 May 2. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 38701778 Free PMC article.
-
Squeezing the eggs to grow: The mechanobiology of mammalian folliculogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 2;10:1038107. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1038107. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36531957 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrostatic pressure as a driver of cell and tissue morphogenesis.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov;131:134-145. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.04.021. Epub 2022 May 6. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35534334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Morphogenetic Roles of Hydrostatic Pressure in Animal Development.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Oct 6;38:375-394. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-120320-033250. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35804476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anani S., Bhat S., Honma-Yamanaka N., Krawchuk D., Yamanaka Y. Initiation of Hippo signaling is linked to polarity rather than to cell position in the pre-implantation mouse embryo. Development. 2014;141:2813–2824. - PubMed
-
- Aziz M., Alexandre H. The origin of the nascent blastocoel in preimplantation mouse embryos: ultrastructural cytochemistry and the effect of chloroquine. Dev. Biol. 1991;200:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

