Rapid Action of Retinoic Acid on the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis
- PMID: 31736706
- PMCID: PMC6831734
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00259
Rapid Action of Retinoic Acid on the Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis
Abstract
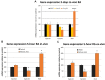
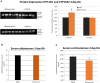
Retinoic acid (RA) is the active metabolite of vitamin A but is also used as a medication, primarily for acne in which the treatment regime lasts several months. A number of studies have indicated that treatment with RA over this time period impacts the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and may contribute to a number of the side-effects of the drug. No studies though have investigated the short-term, early effects RA may have on the HPA axis via the transcriptional pathways activated by the RA receptor. This study investigated the action of RA over 3 days on regulatory components of the HPA axis. Several key genes involved in glucocorticoid feedback pathways in the hippocampus, hypothalamus and pituitary were unchanged after 3-days exposure to RA. Key elements though in the adrenal gland involved in corticosterone and aldosterone synthesis were altered in particular with the Cyp11b2 gene downregulated in vivo and ex vivo. The rapid, 5 h, change in Cyp11b2 expression suggested this activation may be direct. These results highlight the adrenal gland as a target of short-term action of RA and potentially a trigger component in the mechanisms by which the long-term adverse effects of RA treatment occur.
Keywords: Cyp11b1; Cyp11b2; adrenal gland; aldosterone synthesis; corticosterone; hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis; retinoic acid.
Copyright © 2019 Imoesi, Bowman, Stoney, Matz and McCaffery.
Figures
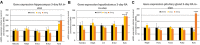
Similar articles
-
Vitamin A regulates hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis status in LOU/C rats.J Endocrinol. 2013 Sep 6;219(1):21-7. doi: 10.1530/JOE-13-0062. Print 2013 Oct. J Endocrinol. 2013. PMID: 23847298
-
Ro41-5253, a selective antagonist of retinoic acid receptor α, ameliorates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depressive-like behaviors in rats: Involvement of regulating HPA axis and improving hippocampal neuronal deficits.Brain Res Bull. 2019 Mar;146:302-309. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.01.022. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Brain Res Bull. 2019. PMID: 30711623
-
Periconceptional ethanol exposure alters the stress axis in adult female but not male rat offspring.Stress. 2019 May;22(3):347-357. doi: 10.1080/10253890.2018.1563068. Epub 2019 Feb 11. Stress. 2019. PMID: 30741061
-
The stress system in the human brain in depression and neurodegeneration.Ageing Res Rev. 2005 May;4(2):141-94. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2005.03.003. Ageing Res Rev. 2005. PMID: 15996533 Review.
-
Activation of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis by cytokines.Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1991;125 Suppl 1:84-91. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh). 1991. PMID: 1801507 Review.
Cited by
-
Control by the brain of vitamin A homeostasis.iScience. 2023 Jul 13;26(8):107373. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107373. eCollection 2023 Aug 18. iScience. 2023. PMID: 37599827 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoid homeostasis in major depressive disorder.Transl Psychiatry. 2023 Feb 23;13(1):67. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02362-0. Transl Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 36813763 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Administration of 13-cis-retinoic Acid Induces Depression-Like Behavior by Altering the Activity of Dentate Granule Cells.Neurotherapeutics. 2022 Jan;19(1):421-433. doi: 10.1007/s13311-021-01168-6. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Neurotherapeutics. 2022. PMID: 34893965 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

