Bee Venom Soluble Phospholipase A2 Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B
- PMID: 31736738
- PMCID: PMC6839038
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00287
Bee Venom Soluble Phospholipase A2 Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B
Abstract
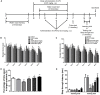
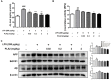
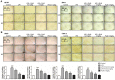
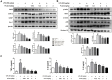
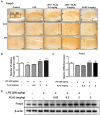
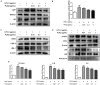
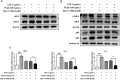
Neuroinflammation is important in the pathogenesis and development of Alzheimer's disease (AD). In the AD brain, microglial activation and upregulation of pro-inflammatory mediators both induce amyloid beta (Aβ) accumulation. Regulatory T cells (Tregs) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling have been implicated in AD development through their effects on neuroinflammation and microglial activation. The bee venom soluble phospholipase A2 (bv-sPLA2) enzyme is known to exert anti-inflammatory and anti-immune effects. Here, we investigated the inhibitory effects of bv-sPLA2 on memory deficiency in a lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced mouse model of AD. We examined whether bv-sPLA2 (0.02, 0.2, and 2 mg/kg by i.p. injection three times for 1 week) could inhibit neuroinflammation and memory impairment in LPS-treated mice (250 μg/kg by i.p. injection daily for 1 week). We also assessed the effects of bv-sPLA2 administration (0.01, 0.1, and 1 μg/ml) on LPS (1 μg/ml)-treated microglial BV-2 cells. In the LPS-injected mouse brain, sPLA2 treatment rescued memory dysfunction and decreased Aβ levels, through the downregulation of amyloidogenic proteins, and decreased the expression of inflammatory proteins and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Moreover, the LPS-mediated increase in inflammatory protein expression was attenuated bv-sPLA2 treatment in BV-2 cells. Treatment with bv-sPLA2 also downregulated signaling by NF-κB, which is considered to be an important factor in the regulation of neuroinflammatory and amyloidogenic responses, both in vivo and in vitro. Additionally, co-treatment with NF-κB (5 μM) and bv-sPLA2 (0.1 μg/ml) exerted more marked anti-inflammatory effects, compared to bv-sPLA2 treatment alone. These results indicate that bv-sPLA2 inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation and amyloidogenesis via inhibition of NF-κB.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; NF-κB; bee venom phospholipase A2; neuroinflammation; regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2019 Ham, Han, Lee, Kim, Yun, Kang, Park, Kim and Hong.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of bee venom and its main components: Recent progress and perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:1001553. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1001553. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bee venom ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced memory loss by preventing NF-kappaB pathway.J Neuroinflammation. 2015 Jun 26;12:124. doi: 10.1186/s12974-015-0344-2. J Neuroinflammation. 2015. PMID: 26112466 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of punicalagin on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB.Neuropharmacology. 2017 May 1;117:21-32. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.01.025. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Neuropharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28132781
-
Inhibitory effect of 4-O-methylhonokiol on lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation, amyloidogenesis and memory impairment via inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB in vitro and in vivo models.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Feb 19;9:35. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-35. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22339795 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of ent-Sauchinone on amyloidogenesis via inhibition of STAT3-mediated NF-κB activation in cultured astrocytes and microglial BV-2 cells.J Neuroinflammation. 2014 Jul 2;11:118. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-11-118. J Neuroinflammation. 2014. PMID: 24985096 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Bee Venom: An Updating Review of Its Bioactive Molecules and Its Health Applications.Nutrients. 2020 Oct 31;12(11):3360. doi: 10.3390/nu12113360. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 33142794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of bee venom and its main components: Recent progress and perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 27;13:1001553. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1001553. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36238572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G721-0282 Exerts Anxiolytic-Like Effects on Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress in Mice Through Inhibition of Chitinase-3-Like 1-Mediated Neuroinflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Mar 7;16:793835. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.793835. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35345530 Free PMC article.
-
Processing Technologies for Bee Products: An Overview of Recent Developments and Perspectives.Front Nutr. 2021 Nov 3;8:727181. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.727181. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34805239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipase A2-A Significant Bio-Active Molecule in Honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Venom.Molecules. 2025 Jun 17;30(12):2623. doi: 10.3390/molecules30122623. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40572586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

