Ethanolic Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Improves Memory in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Model
- PMID: 31736744
- PMCID: PMC6828736
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01216
Ethanolic Extract of Orthosiphon stamineus Improves Memory in Scopolamine-Induced Amnesia Model
Abstract
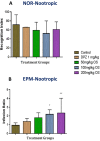
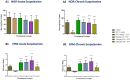
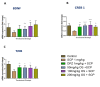
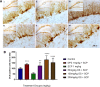
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a chronic neurodegenerative brain disease which is characterized by impairment in cognitive functioning. Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) Benth. (Lamiaceae) is a medicinal plant found around Southeast Asia that has been employed as treatments for various diseases. OS extract contains many active compounds that have been shown to possess various pharmacological properties whereby in vitro studies have demonstrated neuroprotective as well as cholinesterase inhibitory effects. This study, therefore aimed at determining whether this Malaysian plant derived flavonoid can reverse scopolamine induced learning and memory dysfunction in the novel object recognition (NOR) test and the elevated plus maze (EPM) test. In the present study, rats were treated once daily with OS 50 mg/kg, 100 mg/kg, 200 mg/kg and donepezil 1 mg/kg via oral dosing and were given intraperitoneal (ip) injection of scopolamine 1 mg/kg daily to induce cognitive deficits. Rats were subjected to behavioral analysis to assess learning and memory functions and hippocampal tissues were extracted for gene expression and immunohistochemistry studies. All the three doses demonstrated improved scopolamine-induced impairment by showing shortened transfer latency as well as the higher inflexion ratio when compared to the negative control group. OS extract also exhibited memory-enhancing activity against chronic scopolamine-induced memory deficits in the long-term memory novel object recognition performance as indicated by an increase in the recognition index. OS extract was observed to have modulated the mRNA expression of CREB1, BDNF, and TRKB genes and pretreatment with OS extract were observed to have increased the immature neurons against hippocampal neurogenesis suppressed by scopolamine, which was confirmed by the DCX-positive stained cells. These research findings suggest that the OS ethanolic extract demonstrated an improving effect on memory and hence could serve as a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases like AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Orthosiphon stamineus; animal model; learning and memory; scopolamine.
Copyright © 2019 Retinasamy, Shaikh, Kumari and Othman.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelwahab S. I., Mohan S., Mohamed Elhassan M., Al-Mekhlafi N., Mariod A. A., Abdul A. B., et al. (2011). ntiapoptotic and antioxidant properties of Orthosiphon stamineus benth (Cat’s Whiskers): intervention in the Bcl-2-mediated apoptotic pathway. Evid. Based Complementary Alternat. Med. 2011, 156765. 10.1155/2011/156765 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akowuah G. A., Zhari I., Norhayati I., Sadikun A., Khamsah S. M. (2004). Sinensetin, eupatorin, 3′-hydroxy-5, 6, 7, 4′-tetramethoxyflavone and rosmarinic acid contents and antioxidative effect of Orthosiphon stamineus from Malaysia. Food Chem. 87 (4), 559–566. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.01.008 - DOI
-
- Batool Z., Sadir S., Liaquat L., Tabassum S., Madiha S., Rafiq S., et al. (2016). Repeated administration of almonds increases brain acetylcholine levels and enhances memory function in healthy rats while attenuates memory deficits in animal model of amnesia. Brain Res. Bull. 120, 63–74. 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2015.11.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

