Sophocarpine Suppresses NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation Both In Vitro and In Vivo and Inhibits Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 31736745
- PMCID: PMC6836764
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01219
Sophocarpine Suppresses NF-κB-Mediated Inflammation Both In Vitro and In Vivo and Inhibits Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
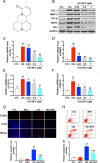
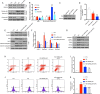
Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a leading cause of mortality in patients with diabetes. DCM is a leading cause of mortality in patients with diabetes. We used both in vitro and in vivo experiments to investigate the hypothesis that sophocarpine (SPC), a natural quinolizidine alkaloid derived from a Chinese herb, could protect against DCM. We used hyperglycemic myocardial cells and a streptozotocin (STZ)-induced type 1 diabetes mellitus mouse model. SPC protected myocardial cells from hyperglycemia-induced injury by improving mitochondrial function, suppressing inflammation, and inhibiting cardiac apoptosis. The SPC treatment significantly inhibited the activation of nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling in high-glucose-stimulated inflammatory responses. Moreover, SPC significantly slowed the development and progression of DCM in STZ-induced diabetic mice. These results show that SPC suppresses NF-κB-mediated inflammation both in vitro and in vivo and may be used to treat DCM.
Keywords: NF-κB; cardiomyopathy—diagnostics; diabetes; inflammation; sophocarpine.
Copyright © 2019 Zou, Wang, Liu, Wang, Hu, Xiong, Wu, Shen and Yang.
Figures



References
-
- Guo Y., Zhuang X., Huang Z., Zou J., Yang D., Hu X., et al. (2018). Klotho protects the heart from hyperglycemia-induced injury by inactivating ROS and NF-kappaB-mediated inflammation both in vitro and in vivo . Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 1864 (1), 238–251. 10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.09.029 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

